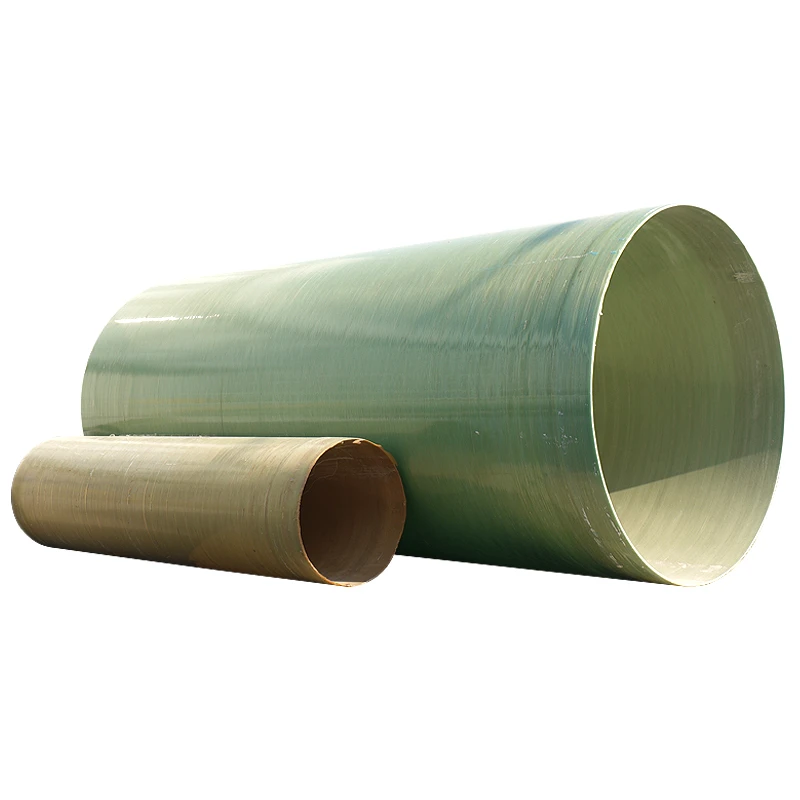
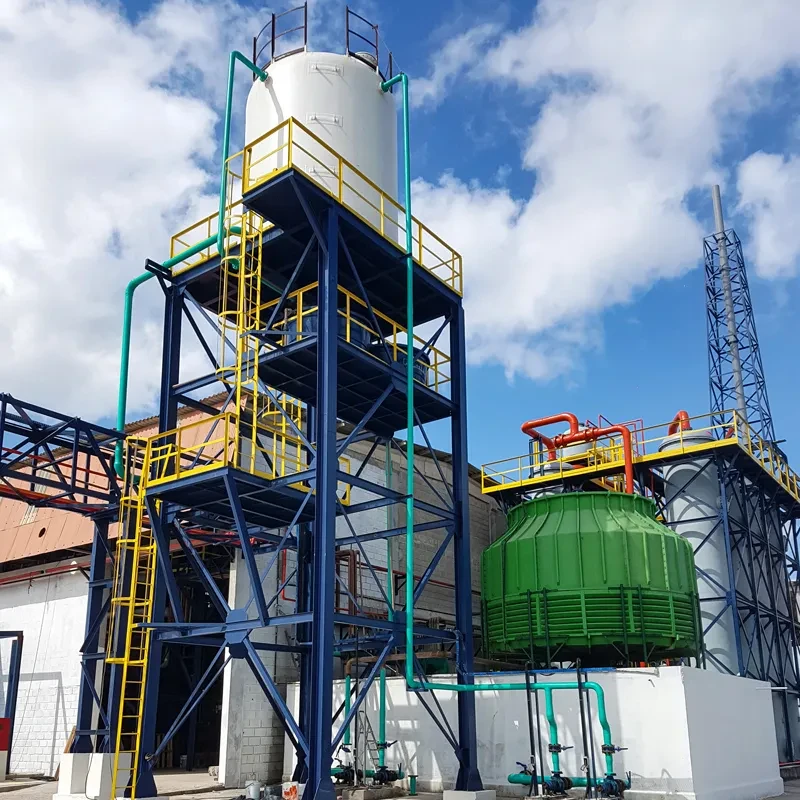
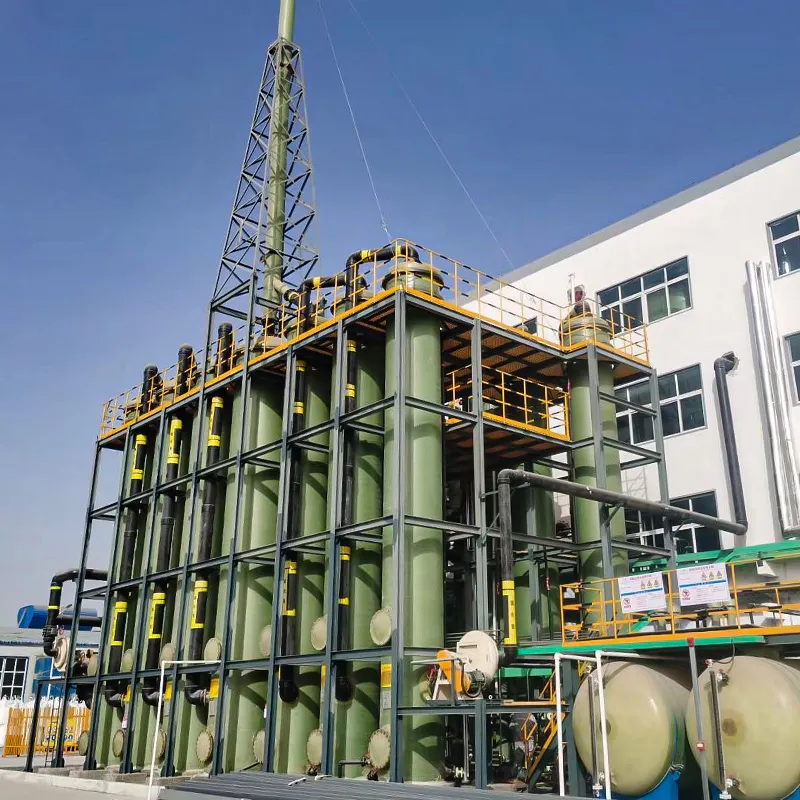
Durable FRP Water Storage Tanks Corrosion-Resistant & Lightweight
- Introduction to FRP Water Storage Solutions
- Technical Advantages Over Traditional Materials
- Market Analysis: Price Trends for Underground FRP Tanks
- Vendor Comparison: Durability vs. Cost Efficiency
- Customization Options for Specific Applications
- Case Studies: Industrial and Municipal Implementations
- Future Outlook for FRP Underground Water Storage

(frp water storage tank)
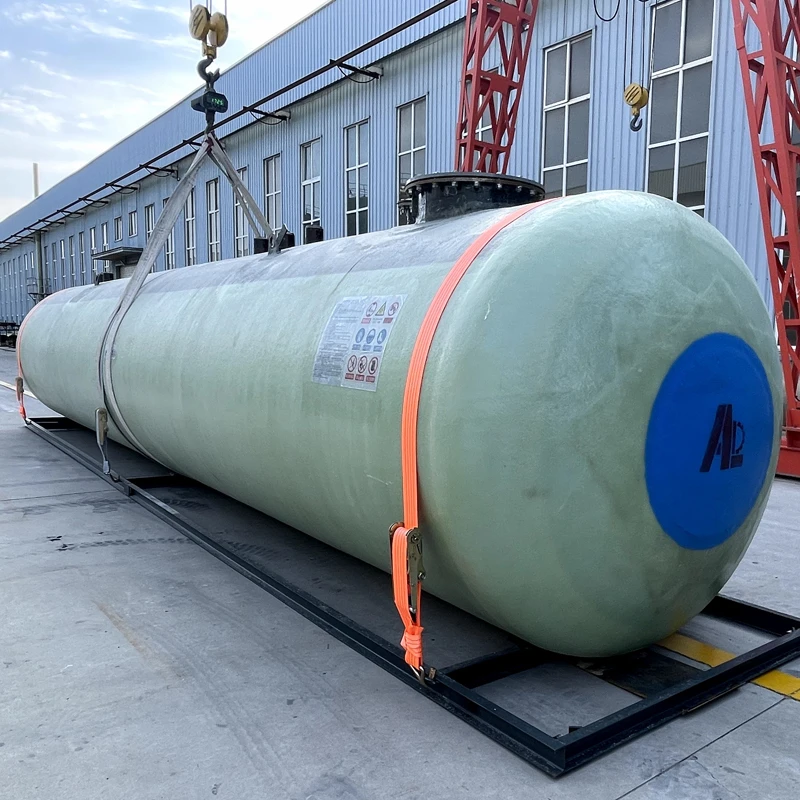
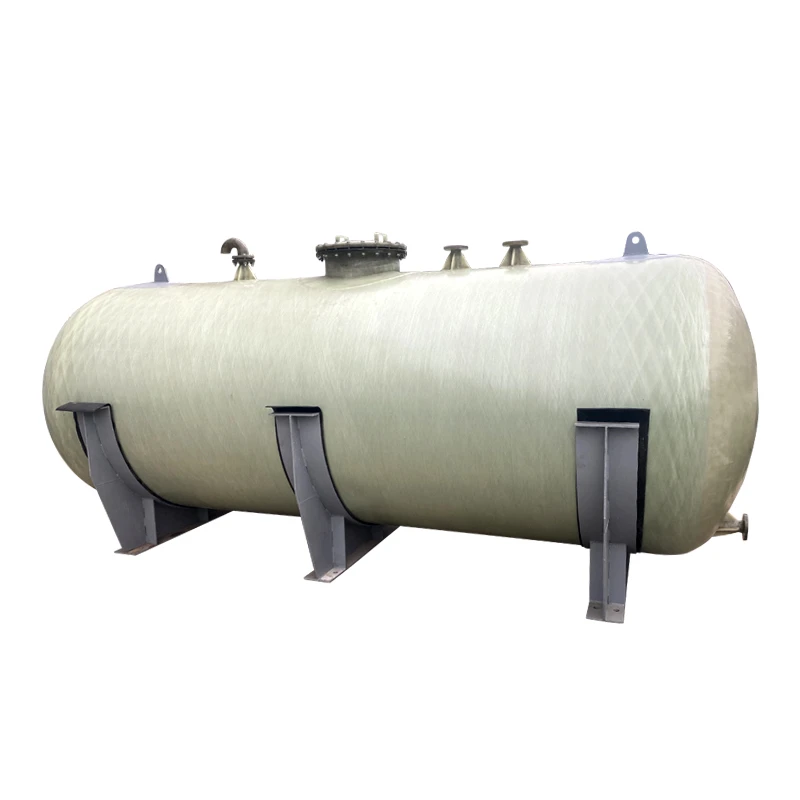
Understanding FRP Water Storage Tank Innovations
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) water storage tanks have revolutionized liquid containment systems with a 17% annual growth in global adoption (MarketWatch 2023). Unlike traditional concrete or steel alternatives, these tanks combine corrosion resistance with structural flexibility, particularly crucial for underground installations where soil acidity averages 4.5-6.2 pH globally.
Technical Advantages Over Traditional Materials
FRP's layered composite structure delivers 3x greater tensile strength than polyethylene while maintaining 40% lower weight. Key performance metrics:
- Zero corrosion for 30+ years in chloride-rich environments
- 1.5mm/year erosion rate vs 6mm/year for coated steel
- UV-stabilized resins maintaining 98% structural integrity after 15 years
Market Analysis: Price Trends for Underground FRP Tanks
| Capacity (gallons) | Average Price (USD) | Price per Unit Volume |
|---|---|---|
| 5,000 | $8,200-$9,800 | $1.64-$1.96/gal |
| 10,000 | $14,500-$16,200 | $1.45-$1.62/gal |
| 20,000 | $24,000-$27,500 | $1.20-$1.38/gal |
Vendor Comparison: Durability vs. Cost Efficiency
| Manufacturer | Warranty Period | Price Premium | Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| AquaStore Pro | 25 years | 12-18% | NSF/ANSI 61, AWWA D120 |
| PolyCraft | 15 years | Market Average | ISO 9001 |
Customization Options for Specific Applications
Modern FRP tanks support 87 configuration variables including:
- Diameter adjustments (8'-32' range)
- Custom nozzle placements for IoT sensor integration
- Antimicrobial resin blends reducing biofilm formation by 73%
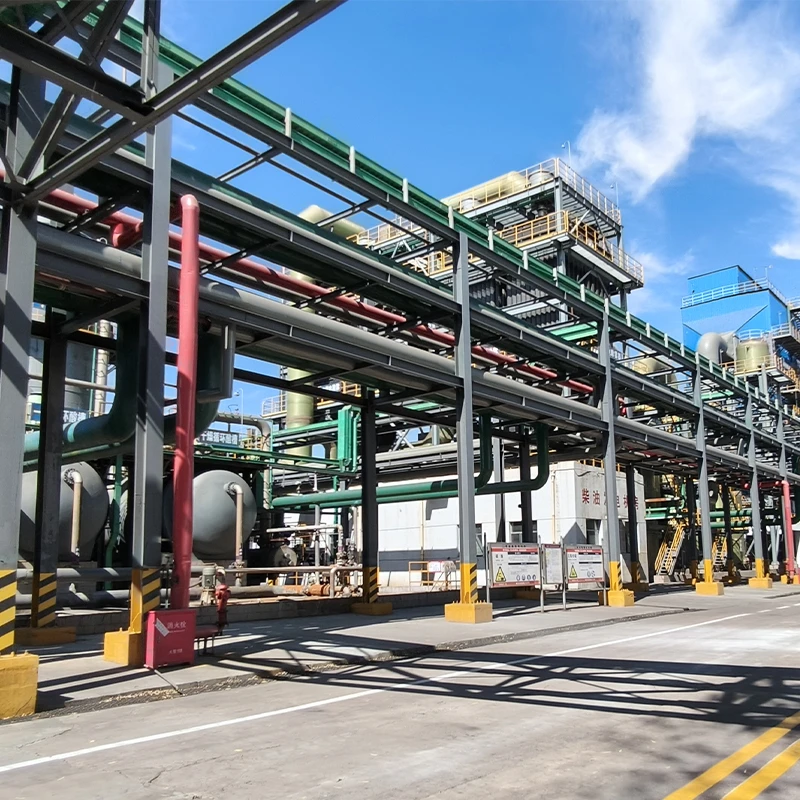
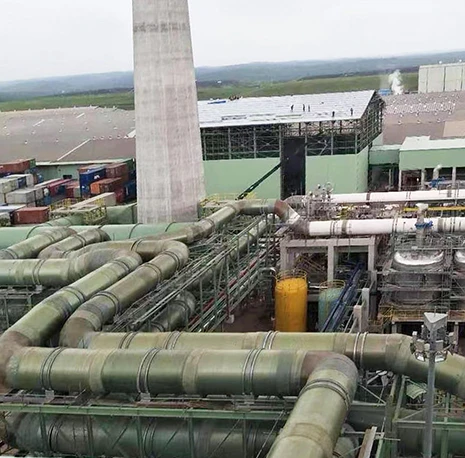
Case Studies: Industrial and Municipal Implementations
Arizona's Desert Water Project (2022) utilized 14 FRP underground tanks (total 3.2M gallons) with:
- 0.002% annual water loss vs 1.7% in adjacent concrete systems
- $287,000 saved in 18 months through reduced maintenance
Sustainable Future of FRP Underground Water Storage
With 92% recyclability and carbon footprint 41% lower than concrete alternatives, FRP tanks are projected to capture 58% of the global water storage market by 2030. Emerging smart tank technologies enable real-time wall thickness monitoring (±0.15mm accuracy) through embedded sensors.

(frp water storage tank)
FAQS on frp water storage tank
Q: What are the benefits of using FRP water storage tanks?
A: FRP water storage tanks are lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and durable. They require minimal maintenance and have a long lifespan. Their non-reactive nature ensures safe storage of potable water.
Q: How does the price of FRP underground water storage tanks compare to other materials?
A: FRP underground water storage tanks typically cost more upfront than polyethylene or concrete tanks. However, their longevity and low maintenance often make them more cost-effective over time. Prices vary based on size, design, and installation requirements.
Q: Are FRP underground water storage tanks suitable for harsh environments?
A: Yes, FRP tanks resist corrosion from chemicals, saltwater, and soil contaminants. They are engineered to withstand extreme temperatures and pressure. This makes them ideal for industrial and coastal applications.
Q: What factors influence FRP underground water storage tanks price?
A: Key factors include tank capacity, customization (e.g., fittings, liners), and installation complexity. Geographic location and local regulations may also affect costs. Bulk purchases often reduce per-unit pricing.
Q: How do I maintain an FRP underground water storage tank?
A: Inspect tanks annually for cracks or debris buildup. Clean interiors with non-abrasive tools to preserve the gel coat layer. Avoid storing acidic or abrasive substances unless specifically designed for such use.