GRP Pipes Durable, Lightweight Sewer & Sleeve Solutions GRP Connection Experts
- Introduction to GRP pipe applications and industry growth
- Technical advantages over traditional materials
- Performance comparison of leading GRP pipe manufacturers
- Customization options for grp pipe
connections and sleeves - Real-world application case studies
- Installation best practices for grp sewer systems
- Future trends in GRP pipe technology

(grp pipe)
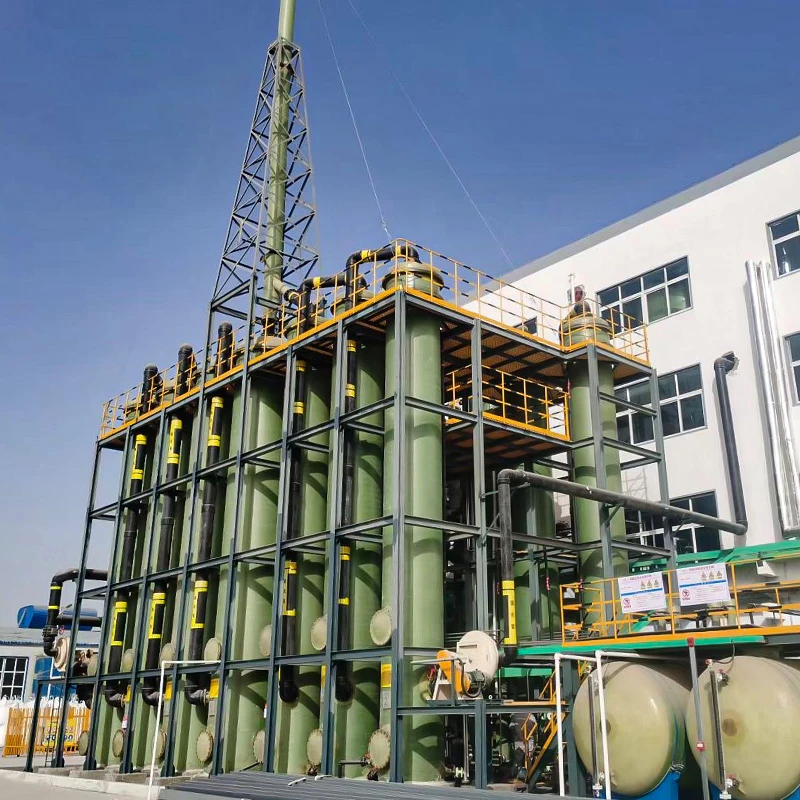
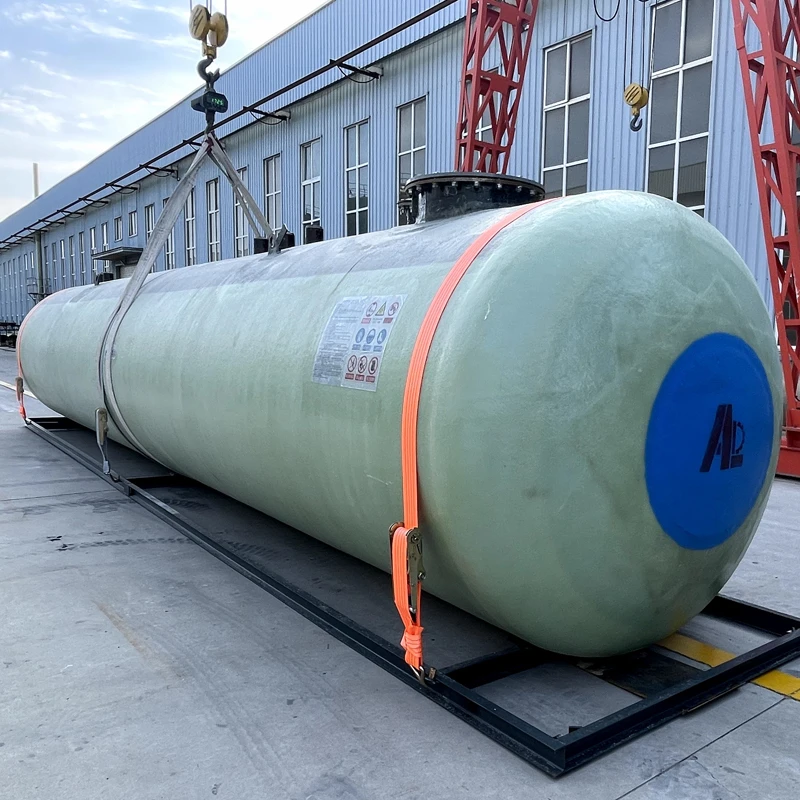
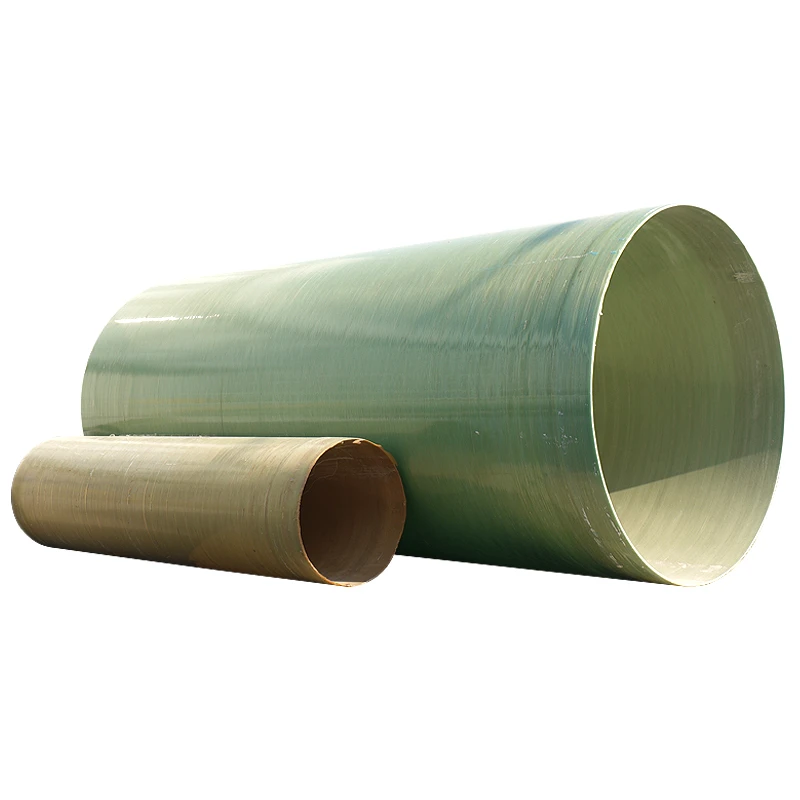
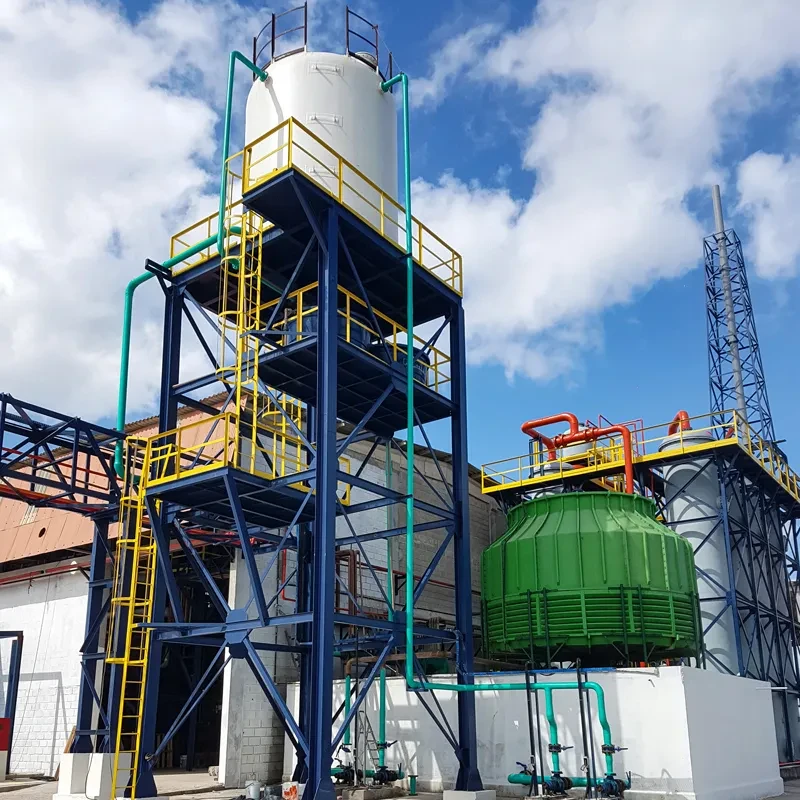
Understanding GRP Pipe Applications in Modern Infrastructure
The global GRP pipe market is projected to grow at a 6.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by demand for corrosion-resistant solutions. Unlike traditional materials, GRP (Glass Reinforced Plastic) combines high tensile strength (350-500 MPa) with a lifespan exceeding 50 years, making it ideal for sewer systems and industrial applications. Recent studies show GRP sewer pipes reduce maintenance costs by 40% compared to concrete alternatives.
Technical Superiority of Composite Materials
GRP’s layered structure provides unique benefits:
- Weight reduction: 70% lighter than steel pipes
- Chemical resistance: Withstands pH 1-13 environments
- Flow efficiency: Hydraulic smoothness (Hazen-Williams coefficient: 150)
Manufacturer Performance Benchmarking
| Vendor | Tensile Strength | Max Diameter | Temp Range | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | 480 MPa | 3600 mm | -40°C to 80°C | 25 years |
| Company B | 420 MPa | 2800 mm | -30°C to 75°C | 20 years |
| Company C | 510 MPa | 4000 mm | -50°C to 85°C | 30 years |
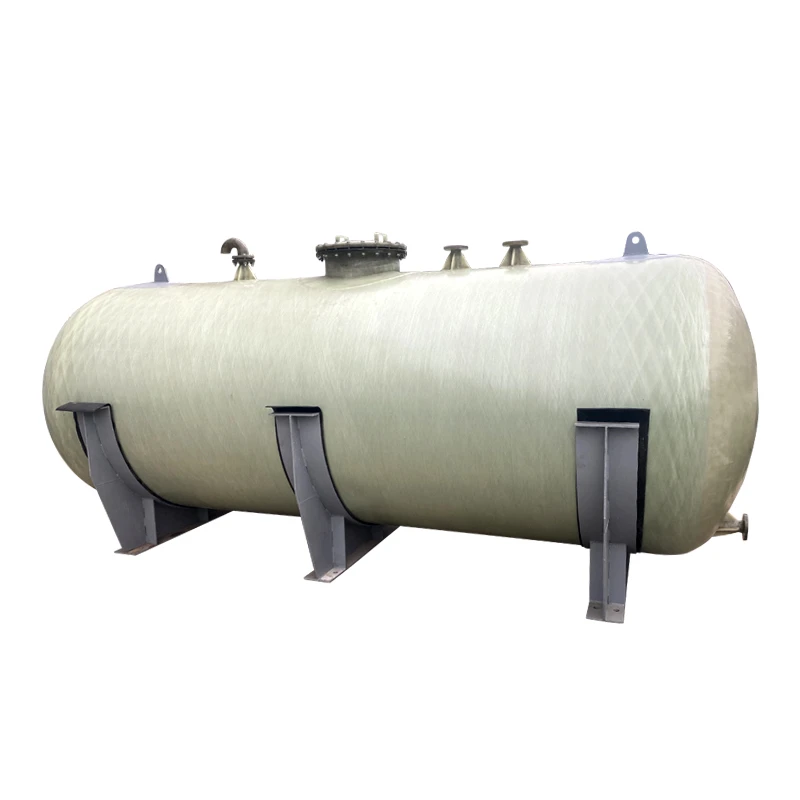
Tailored Solutions for Complex Installations
Advanced GRP pipe connections now offer:
- Modular coupling systems with ±5° angular deflection
- Custom sleeve diameters from 100 mm to 4 m
- Electrofusion joints for leak-proof sealing
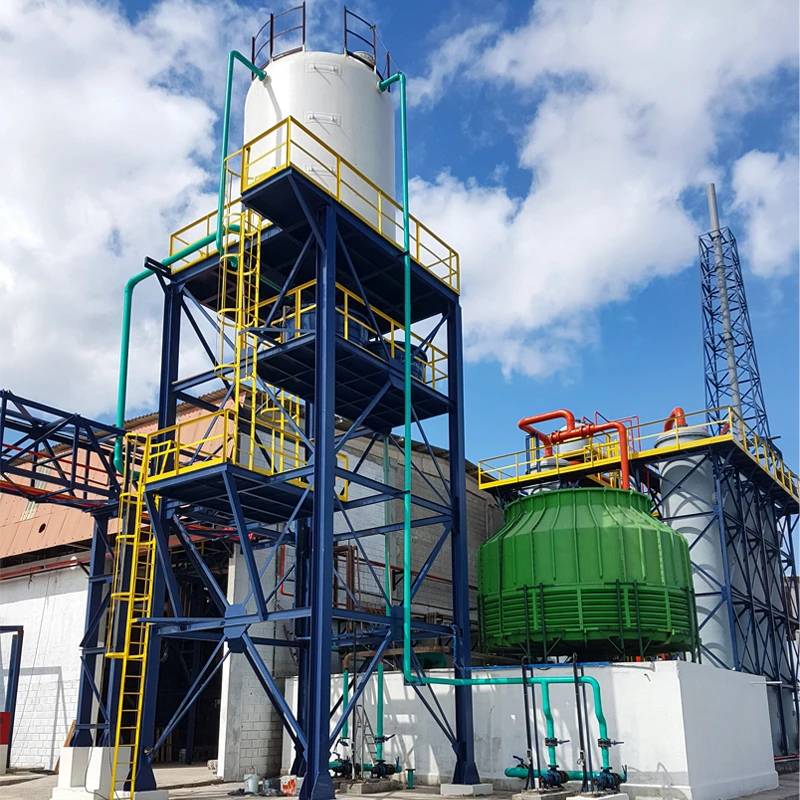
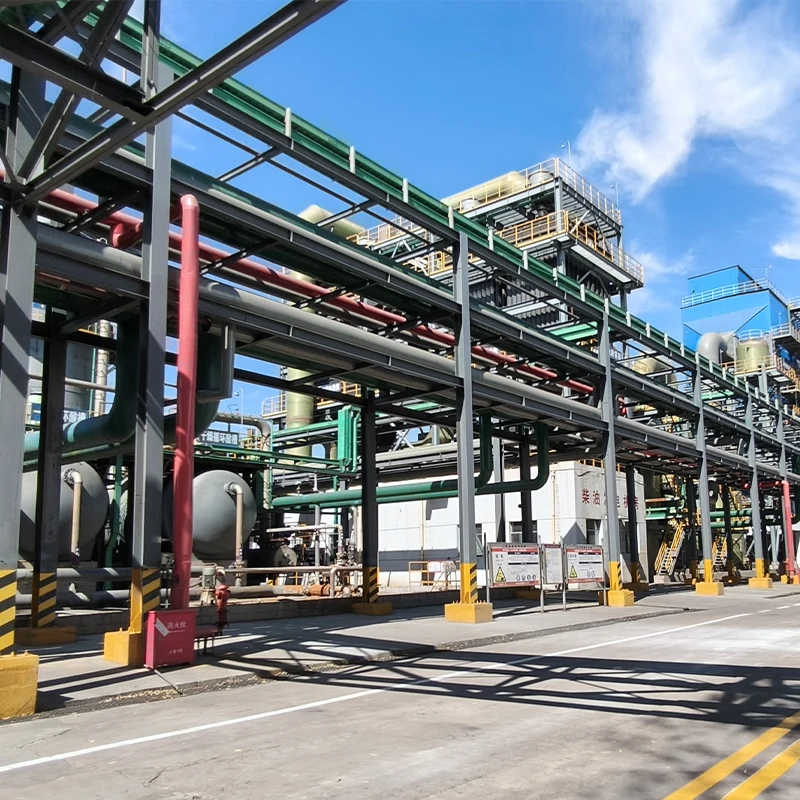
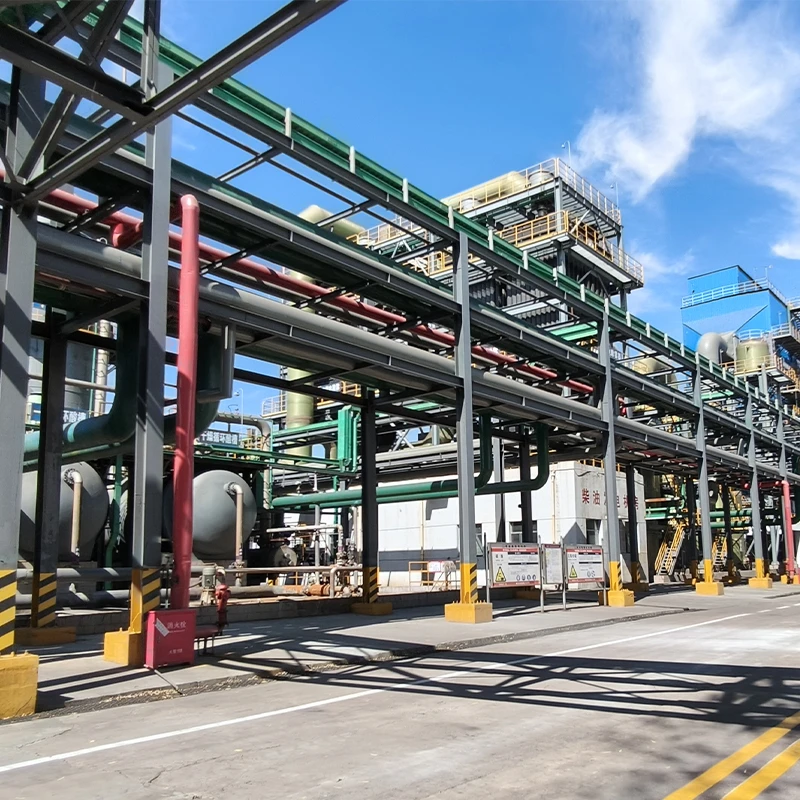
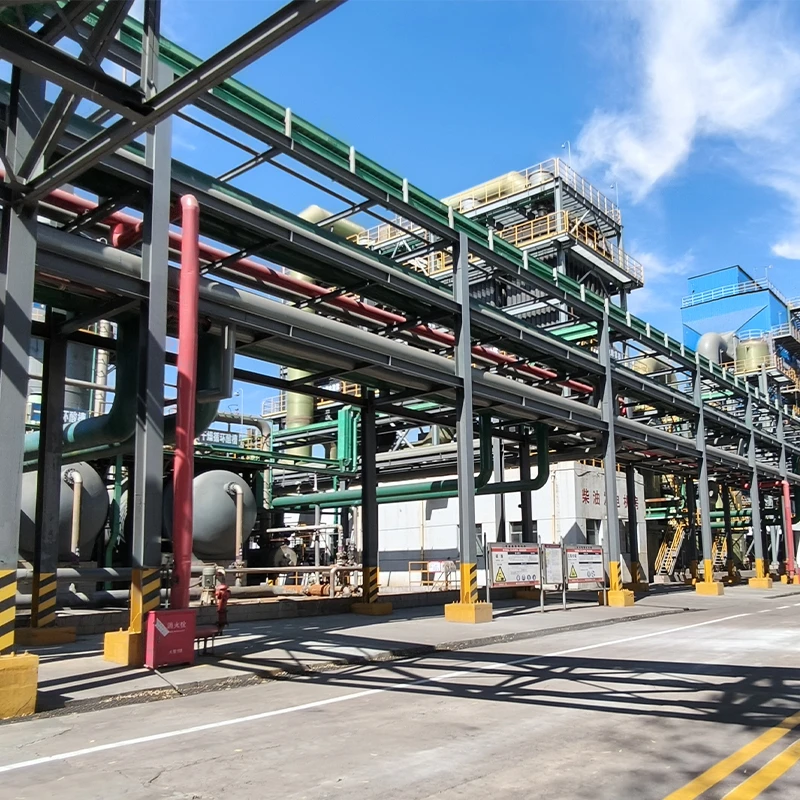
Proven Success in Challenging Environments
Notable GRP sewer pipe deployments include:
- Coastal wastewater network (Middle East): 12 km system resisting 5% salinity
- Geothermal plant (Iceland): GRP connections enduring 80°C effluent
- Mining operation (Chile): Abrasion-resistant sleeves lasting 3x longer than steel
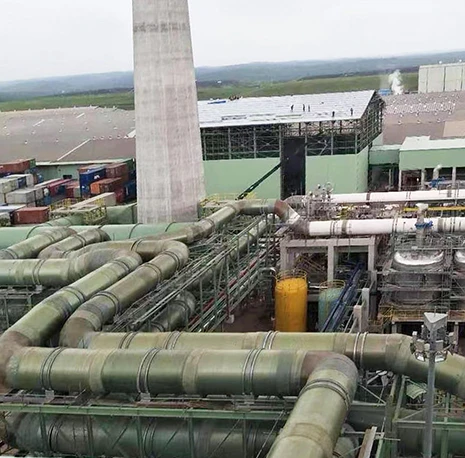
Optimizing GRP Sewer System Installations
Proper installation extends service life by 35%:
- Bedding preparation: Angular substrate with ≤12 mm particles
- Joint alignment: Laser-guided positioning within 2 mm tolerance
- Backfill compaction: 95% Proctor density achieved through layered compaction
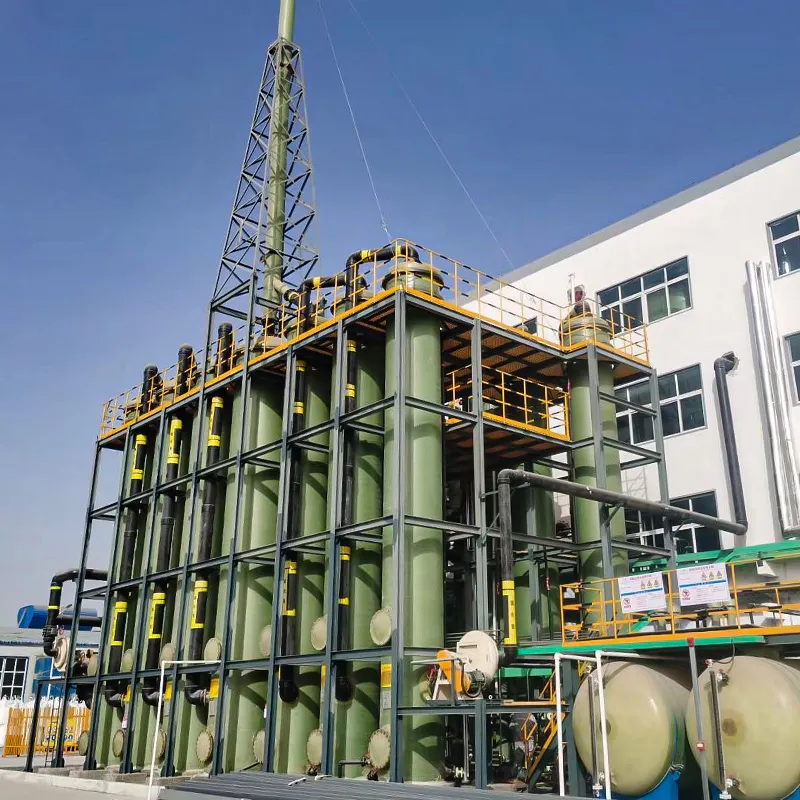
GRP Pipe Innovations Driving Sustainable Infrastructure
Emerging technologies in GRP pipe manufacturing include:
- Smart liners with embedded fiber optics for real-time monitoring
- Bio-resin composites reducing carbon footprint by 60%
- 3D-printed connection interfaces for complex geometries

(grp pipe)
FAQS on grp pipe
Q: What are the key advantages of using GRP pipes in industrial applications?
A: GRP pipes offer high corrosion resistance, lightweight construction, and long-term durability. Their non-conductive properties and customizable designs make them ideal for harsh environments like chemical plants or wastewater systems.
Q: How does a GRP sewer pipe handle aggressive wastewater environments?
A: GRP sewer pipes use resin-rich inner layers to resist chemical corrosion and abrasion. Their smooth surface minimizes biofilm buildup, ensuring consistent flow efficiency in sewage and industrial effluent systems.
Q: What methods ensure secure GRP pipe connections?
A: GRP pipe connections typically use flange joints, socket-and-spigot systems, or adhesive bonding. Proper surface preparation, alignment checks, and curing of jointing materials are critical for leak-proof performance.
Q: When should GRP sleeve pipes be used in pipeline projects?
A: GRP sleeve pipes are ideal for trenchless rehabilitation of damaged pipelines or as protective casings. They provide structural reinforcement while resisting soil stresses and electrochemical degradation in underground installations.
Q: Can GRP pipes be joined to other pipe materials?
A: Yes, GRP pipes can connect to metal or concrete pipes using transition adapters. Specialized flange designs or rubber-sealed couplers maintain structural integrity while accommodating different thermal expansion rates.