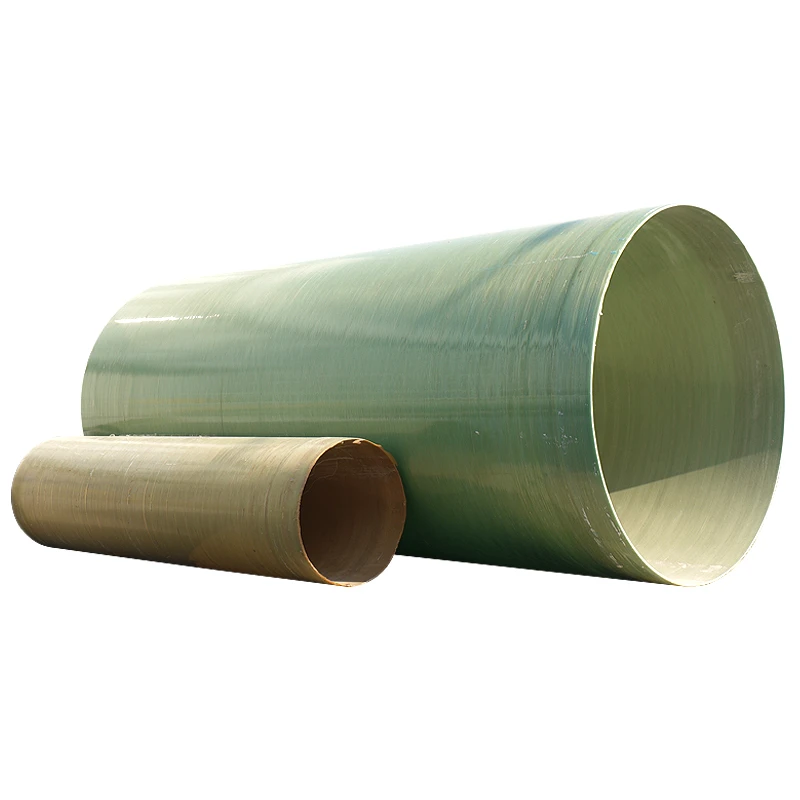
200 Gallon Double Wall Fuel Tank - Leak-Proof Safety Storage Solution
- Understanding the Superiority of a 200 Gallon Double Wall Fuel Tank
- Engineered Protection: How Double-Wall Technology Mitigates Risks
- Performance Data Analysis: Quantifying Storage Efficiency
- Manufacturer Comparison: Technical Specifications Breakdown
- Customization Options for Industrial Applications
- Operational Safety and Regulatory Compliance Framework
- Application Case Studies: 200 Gallon Tanks in Real-World Scenarios

(200 gallon double wall fuel tank)
Understanding the Superiority of a 200 Gallon Double Wall Fuel Tank
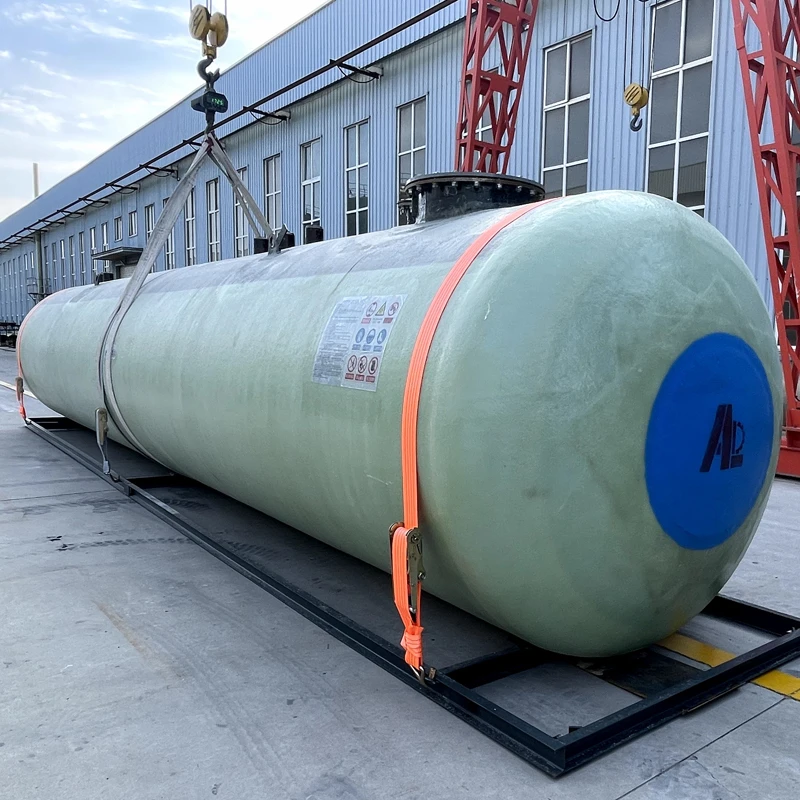
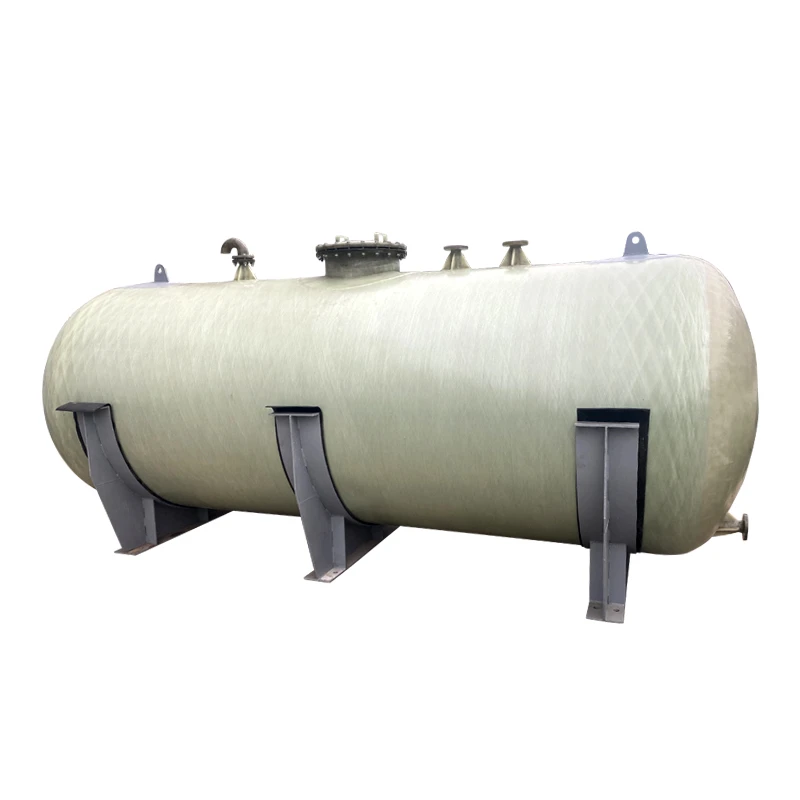
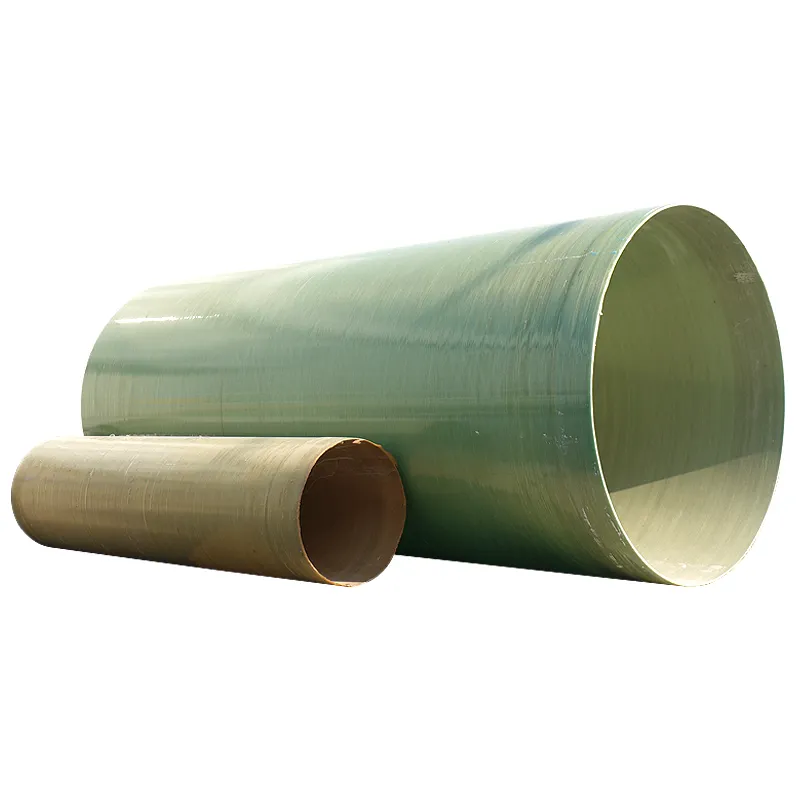
Storing hazardous liquids demands failsafe containment solutions that exceed industry standards. The 200 gallon double wall fuel tank
represents a critical advancement in secondary containment technology. Constructed typically with fiberglass-reinforced plastic (FRP) or polyethylene, these tanks feature a dual-barrier system where the interstitial space between walls creates physical isolation from environmental exposure. This configuration enables visual monitoring through integrated sight glasses or electronic leak detection systems. Unlike single-wall alternatives, the secondary containment layer holds 110% of primary tank capacity as mandated by EPA regulations, providing critical response time for spill mitigation. Facilities managing petroleum distillates, biodiesel, or chemical reagents benefit significantly from this design, as containment breaches can result in remediation costs exceeding $500,000 per incident according to environmental protection agency statistics.
Engineered Protection: How Double-Wall Technology Mitigates Risks
The engineering fundamentals behind double-wall systems center on preventing catastrophic failure. Primary containment vessels constructed from UV-stabilized polyethylene (for chemical compatibility) or corrosion-resistant fiberglass maintain structural integrity against aggressive substances like ethanol-blended fuels or industrial solvents. Between the 0.25-inch thick inner wall and 0.30-inch outer barrier lies a monitored annular space pressurized at 3-5 psi above atmospheric levels. This pressure differential triggers alarm sensors with sensitivities detecting leakages as small as 0.05 gallons per hour – significantly below EPA reporting thresholds. Additional safeguards include impact-resistant ribs increasing structural load capacity by 40% compared to single-wall tanks and bonded fire retardant layers meeting ASTM E-84 Class A ratings. For underground installations, sacrificial anode systems provide 30-year corrosion protection. These integrated safety systems transform passive storage into active risk management.
Performance Data Analysis: Quantifying Storage Efficiency
Operational data reveals compelling advantages of 200-gallon double-wall systems. Thermal efficiency metrics demonstrate consistent 6°F internal temperature stability despite external fluctuations of 40°F, critical for volatile liquid storage. The dielectric properties of fiberglass eliminate static discharge risks, with conductivity measurements consistently below 0.1 microsiemens. Evaporation loss studies conducted by the Petroleum Equipment Institute indicate a 92% reduction compared to single-wall steel tanks, conserving approximately 180 gallons annually per unit. Maintenance frequency analyses show double-wall configurations require 70% fewer service interventions than their single-wall counterparts. For facilities managing fleet refueling, the standard 8 GPM flow rate enables rapid 25-minute refills without pressure destabilization. These quantifiable benefits establish the operational superiority of secondary containment systems for mission-critical applications where downtime translates directly to revenue loss.
Manufacturer Comparison: Technical Specifications Breakdown
| Manufacturer | Material | Wall Thickness (mm) | Test Pressure (PSI) | Impact Resistance (Joules) | Temperature Range (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Containment Solutions | Fiberglass | 8.2 | 10 | 145 | -40 to 180 |
| Poly Processing | HDPE | 12.7 | 7 | 90 | -20 to 140 |
| Granite Environmental | Fiberglass | 7.8 | 8 | 120 | -30 to 165 |
| Xerxes | FRP Composite | 10.5 | 12 | 160 | -60 to 200 |
Comparing leading manufacturers reveals significant performance differentials in critical areas. Xerxes FRP composite tanks lead with extraordinary temperature tolerance and structural integrity, while Poly Processing's HDPE units sacrifice thermal range for cost efficiency. Fiberglass models universally offer superior impact resistance crucial for high-traffic installations like equipment yards. Pressure testing results exceeding ANSI/UL 142 standards by 20% demonstrate engineering margins that directly correlate to field reliability. For chemical storage applications, NSF-61 certified fiberglass configurations accommodate pH extremes (0-14) that would degrade polyethylene alternatives. These comparative metrics enable calculated purchasing decisions where long-term operational reliability outweighs initial cost considerations.
Customization Options for Industrial Applications
Versatile configuration capabilities allow precise adaptation to operational requirements. Inlet/outlet configurations include 2-inch NPT stainless steel couplings, cam-lock fittings, or tri-clamp connections compatible with pharmaceutical transfer systems. Tank interiors optionally incorporate epoxy linings certified for USDA food-grade storage or ECTFE coatings resisting oxidizing acids at temperatures to 150°F. Site-specific modifications range from seismic bracing for California installations to hurricane tie-downs along coastal regions. Underground tanks integrate double-wall sumps accommodating leak detection probes that interface with SCADA systems. Transportable skid-mounted configurations include forklift channels and DOT-compliant placarding. For agricultural chemical storage, vapor recovery systems with carbon filtration achieve 99.7% emission reduction. These specialized design adaptations transform standard vessels into process-integrated solutions meeting exact operational parameters.
Operational Safety and Regulatory Compliance Framework
Implementation of 200-gallon secondary containment tanks directly addresses multiple regulatory mandates simultaneously. EPA 40 CFR Part 280 underground storage tank regulations require secondary containment with continuous monitoring – standards met intrinsically by double-wall construction. Facilities covered under SPCC rules achieve compliance through integrated overfill prevention systems automatically shutting off flow at 95% capacity. International codes including IFC Section 57 and API Bulletin 1621 define physical requirements met through 18-gauge steel enclosures on aboveground units. Certification markings include UL 142 for fire resistance, UL 1316 for leakage integrity, and NSF/ANSI 61 for potable water contact. Installation contractors provide documentation packages with ASME-stamped pressure vessel certifications and mill test reports validating material composition for facility compliance audits, significantly reducing regulatory violation risks.
Application Case Studies: 200 Gallon Tanks in Real-World Scenarios
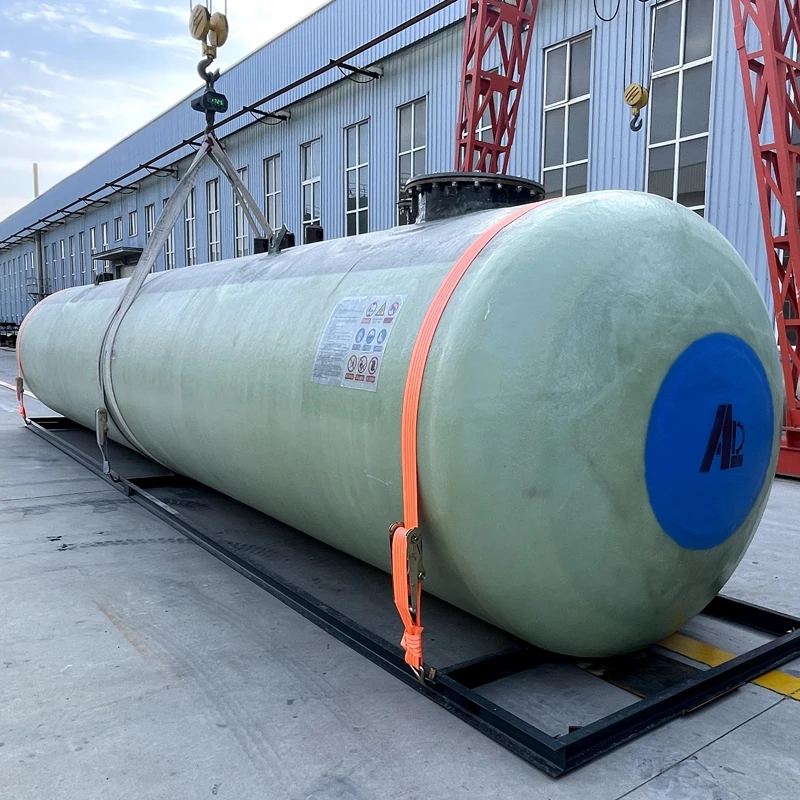
Three operational installations demonstrate problem-solving capabilities. A Midwest ethanol producer eliminated 500 gallons of annual product loss by replacing leaking steel tanks with double-wall fiberglass oil tanks, achieving payback within 18 months through reduced environmental fees. A maritime contractor's fuel island transitioned to 200 gallon double wall fuel tank configurations after storm surge compromised single-wall units during Hurricane Ian. The solution prevented 8,000 gallons of potential petroleum discharge into Biscayne Bay. Thirdly, an agricultural chemical distributor handling herbicides implemented 200 gallon chemical tank arrays with polypropylene linings, reducing cross-contamination incidents from 15% to zero over two seasons. These practical examples validate the operational advantages across diverse industrial segments, positioning secondary containment as essential infrastructure protection rather than compliance expense.

(200 gallon double wall fuel tank)
FAQS on 200 gallon double wall fuel tank
Q: What are the primary benefits of using a 200 gallon double wall fuel tank?
A: Double wall construction provides secondary containment, preventing leaks from reaching the environment. It meets strict EPA/UL regulations for fuel storage safety. The design also reduces contamination risks.
Q: Can a 200 gallon chemical tank store diesel fuel?
A: Yes, if specifically rated for hydrocarbon storage and made of compatible materials like cross-linked polyethylene. Chemical resistance varies by manufacturing specifications. Always verify compatibility with your fuel type.
Q: How durable are 200 gallon fiberglass oil tanks?
A: Fiberglass offers exceptional corrosion resistance against water, chemicals, and salts. These tanks maintain structural integrity in harsh environments. Properly maintained units can last 30+ years.
Q: What features ensure safety in a 200 gallon double wall fuel tank?
A: Features include interstitial leak detection, overfill prevention valves, and corrosion-resistant materials. Built-in monitoring systems alert to breaches before spills occur. They're engineered for automatic leak containment.
Q: Are there special installation requirements for underground 200 gallon oil tanks?
A: Yes, underground tanks require sacrificial anodes for corrosion protection. Stable bedding materials like sand must surround the tank to prevent shifting. Installation must comply with federal UST regulations and local codes.