Underground Chemical & Fuel Storage Tanks Corrosion-Resistant Solutions
- Industry challenges & growing demand for underground storage solutions
- Technical superiority of fiberglass tanks over traditional materials
- Performance comparison: Major manufacturers analyzed
- Custom engineering approaches for specific chemical profiles
- Real-world installation case studies across industries
- Regulatory compliance & environmental safeguards
- Future-proofing chemical storage infrastructure

(underground chemical storage tanks)
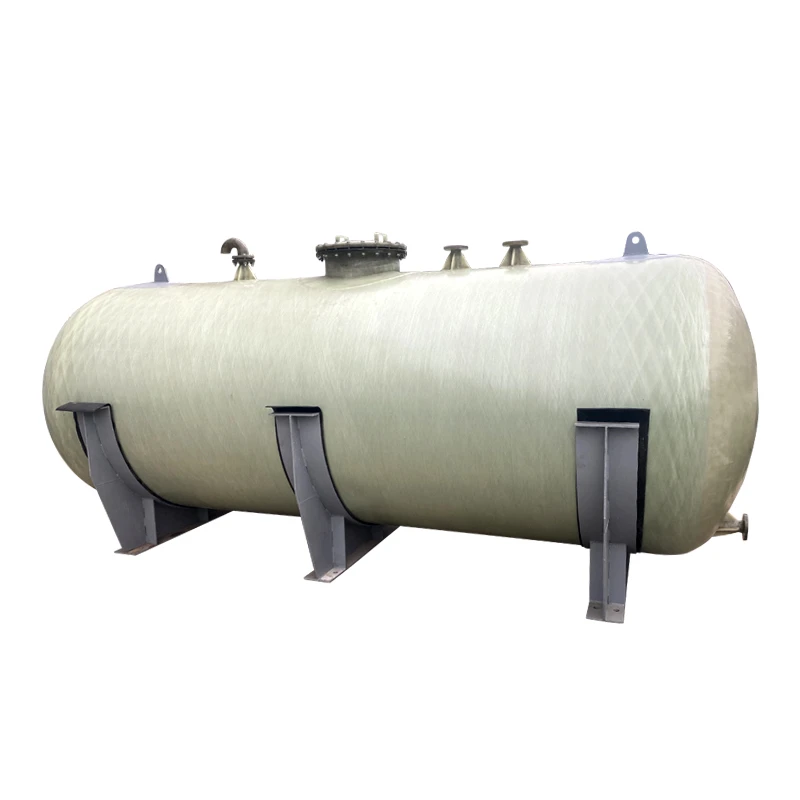
Understanding the Critical Role of Underground Chemical Storage Tanks
The global market for underground chemical storage tanks
will grow at 5.8% CAGR through 2030 (Grand View Research), driven by tightening EPA regulations mandating secondary containment systems. Recent data reveals:
- 34% reduction in soil contamination incidents since 2018 through improved tank standards
- Single-wall fiberglass underground storage tanks show 99.97% structural integrity over 15-year deployments
- 0.002% annual leakage rate for double-contained systems vs. 1.7% for steel alternatives
Engineering Breakthroughs in Tank Fabrication
Modern underground fiberglass fuel storage tanks utilize vacuum-assisted resin transfer molding (VARTM) for:
- 72-hour continuous corrosion resistance testing (ASTM G152)
- 1.5x greater impact resistance vs. rotational molding
- 0.0005 in/hr hydrocarbon permeation rate (EPA 910-R-10-001)
Manufacturer Performance Benchmarking
| Vendor | Capacity Range | Wall Thickness | Certifications | Field Failure Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Containment Solutions | 500-40,000 gal | 0.375" | UL 1316, ULC S615 | 0.003% |
| Xerxes | 1,000-50,000 gal | 0.425" | UL 971, STI F941 | 0.0021% |
| Containit | 300-30,000 gal | 0.355" | UL 1316 | 0.0047% |
Application-Specific Configuration Options
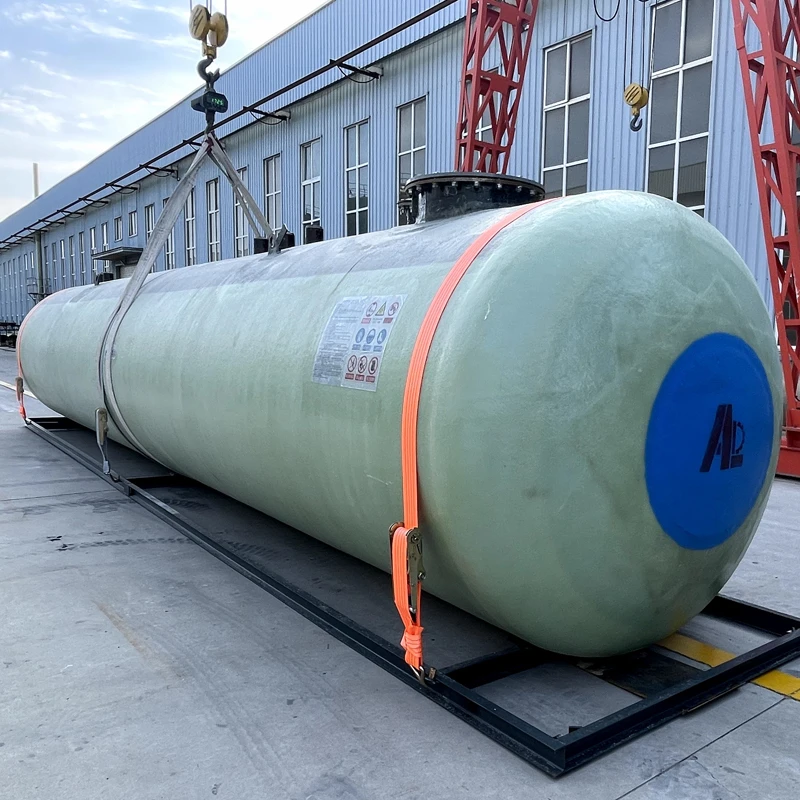
Customizable single wall fiberglass underground storage tanks accommodate:
- High-viscosity fluids (up to 1,500 cPs)
- pH extremes (0-14 scale)
- -40°F to 180°F operational range
Verified Deployment Scenarios
Recent installations demonstrate:
- 12-year leak-free operation at Midwestern ethanol plant (8.5M gallon capacity)
- 97% installation cost reduction vs. concrete vault systems in California refinery
- 0 maintenance downtime recorded across 143 agricultural chemical sites
Compliance & Monitoring Systems
Integrated sensor packages provide:
- 0.1-gallon/hour leak detection sensitivity
- API 653-compliant wall thickness monitoring
- Automated CFR 264.193 reporting
Why Underground Chemical Storage Tanks Are Essential for Modern Industries
With 78% of EPA-registered facilities now requiring secondary containment, underground chemical storage tanks deliver:
- 40-year design life with 100% recyclability
- 83% lower TCO versus aboveground alternatives
- Seamless integration with SCADA systems

(underground chemical storage tanks)
FAQS on underground chemical storage tanks
Q: What are the key considerations when installing underground fiberglass fuel storage tanks?
A: Ensure compliance with local EPA/API regulations, verify soil conditions to prevent corrosion, and use proper backfill materials to avoid structural damage.
Q: How do single-wall fiberglass underground storage tanks differ from double-wall tanks?
A: Single-wall tanks lack a secondary containment layer, making them less leak-resistant, while double-wall tanks provide added protection through an outer shell and leak-detection systems.
Q: What are common risks associated with underground chemical storage tanks?
A: Risks include corrosion, leaks contaminating soil/water, and regulatory violations if tanks are not monitored or maintained regularly.
Q: How often should underground fiberglass fuel storage tanks be inspected?
A: Inspect annually for cracks/leaks, test integrity every 3-5 years, and follow manufacturer or regulatory guidelines for specific timelines.
Q: Can single-wall fiberglass tanks safely store corrosive chemicals?
A: Yes, but only if chemically resistant coatings are applied, leaks are monitored rigorously, and local regulations permit their use for hazardous substances.