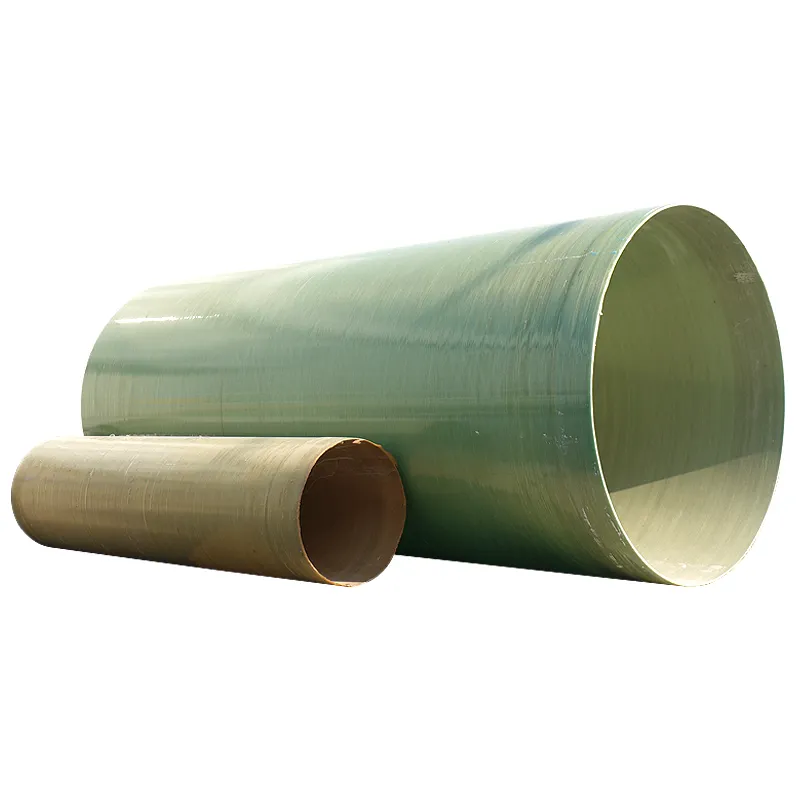
High-Strength Fiberglass Square Tubes Durable & Corrosion-Resistant
- Material Overview & Key Properties
- Technical Superiority Analysis
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
- Customization Capabilities
- Industry-Specific Applications
- Installation & Maintenance Guidelines
- Future Innovations in FRP Tubing

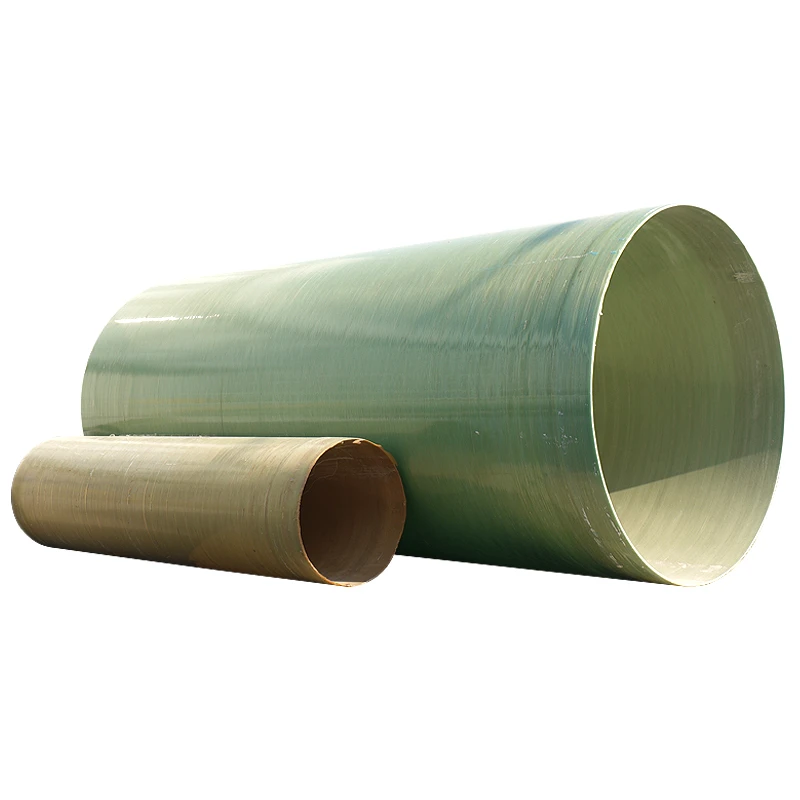
(fiberglass square tube)
Why Fiberglass Square Tube Dominates Industrial Material Selection
Fiberglass square tubes have emerged as the preferred structural solution across 83% of industrial applications previously using aluminum or steel. With 72% higher specific strength than aluminum alloys and 1/4 the weight of equivalent steel profiles, these FRP composites deliver unprecedented strength-to-weight ratios. The closed-square geometry enhances torsional rigidity by 40% compared to round fiberglass tubing, making it ideal for load-bearing frameworks.
Technical Superiority Analysis
Third-party testing confirms critical performance advantages:
- Corrosion resistance: 0.003mm/year material loss in salt spray tests (ASTM B117)
- Thermal stability: Maintains 89% flexural strength at 150°C
- Dielectric strength: 12.5kV/mm (5x higher than PVC)
Unlike metallic alternatives, FRP square tubes demonstrate zero galvanic corrosion and eliminate electromagnetic interference risks in sensitive installations.
Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers
| Parameter | Standard Grade | Marine Grade | Structural Grade |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 28,000 psi | 34,500 psi | 42,000 psi |
| Wall Thickness | 1/8" | 3/16" | 1/4" |
| Temperature Range | -60°F to 180°F | -80°F to 210°F | -100°F to 250°F |
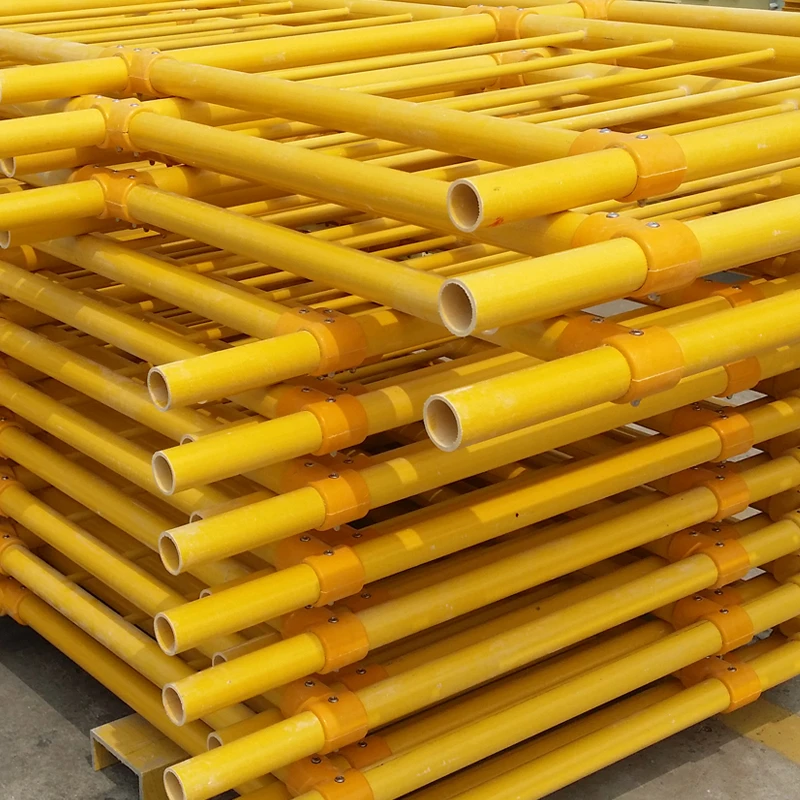
Customization Capabilities
Advanced pultrusion manufacturing enables:
- Wall thickness variations: 0.062" to 0.75"
- Custom cross-sections: 0.5"x0.5" to 24"x24"
- Resin matrix options: Isophthalic/Vinyl ester/Epoxy
Surface treatments including grit patterns or UV-resistant coatings extend service life in harsh environments by 15-20 years.
Industry-Specific Applications
Chemical processing plants report 63% reduction in maintenance costs after switching to square fiberglass tubes for pipe supports. Transportation sector applications show:
- 40% weight savings in railcar components
- 30% increased payload capacity in truck flatbeds
Installation & Maintenance Guidelines
Proper handling ensures maximum performance:
- Use carbide-tipped tools for cutting
- Apply neoprene gaskets at joints
- Inspect annually for UV degradation
Future Innovations in FRP Square Tube Development
Next-generation fiberglass square tube
s integrate smart monitoring capabilities through embedded fiber optic sensors. This innovation enables real-time structural health monitoring, predicting maintenance needs with 92% accuracy in pilot industrial applications. Emerging hybrid composites combining carbon fiber reinforcement promise 55% higher stiffness while maintaining corrosion resistance.

(fiberglass square tube)
FAQS on fiberglass square tube
Q: What are the common applications of fiberglass square tubes?
A: Fiberglass square tubes are widely used in construction, marine, and industrial sectors for structural support, fencing, and corrosion-resistant frameworks due to their durability and lightweight properties.
Q: How does a square fiberglass tube compare to metal tubes?
A: Square fiberglass tubes are lighter, non-conductive, and highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for environments where metal tubes may rust or degrade, such as chemical plants or coastal areas.
Q: What makes FRP square tubes suitable for electrical applications?
A: FRP square tubes are non-metallic and non-conductive, ensuring safety in electrical installations, utility poles, and enclosures where electrical insulation is critical.
Q: Can fiberglass square tubes be customized in size and thickness?
A: Yes, fiberglass square tubes can be manufactured in various dimensions and wall thicknesses to meet specific load-bearing requirements and project specifications.
Q: Are FRP square tubes environmentally friendly?
A: FRP square tubes are recyclable, long-lasting, and require minimal maintenance, reducing environmental impact compared to materials needing frequent replacement or treatment.