Mannheim Furnace: A Core Equipment For Sulfuric Acid Production
Mannheim Furnace, Also called potassium sulfate reactor, it is a key equipment for industrial production of sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, especially playing an important role in the early development of sulfuric acid industry. It reacts sodium chloride (table salt) with sulfuric acid through high-temperature reaction to generate sodium sulfate and hydrochloric acid gas, providing raw materials for further production of sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid. Although the modern sulfuric acid industry is gradually shifting towards more advanced production processes, Mannheim Furnaces still have certain value in certain specific applications and regions.
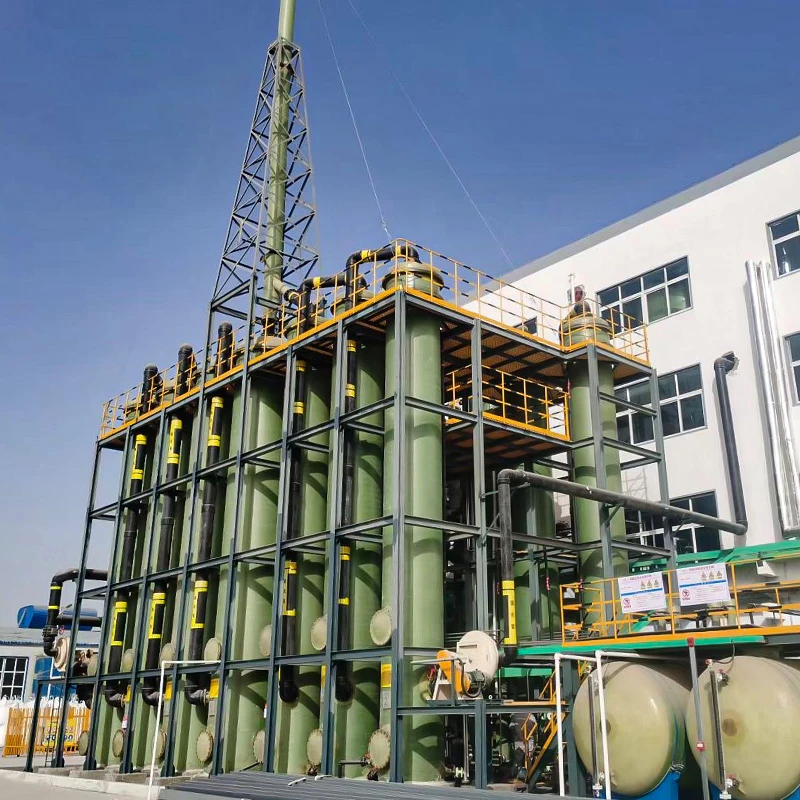
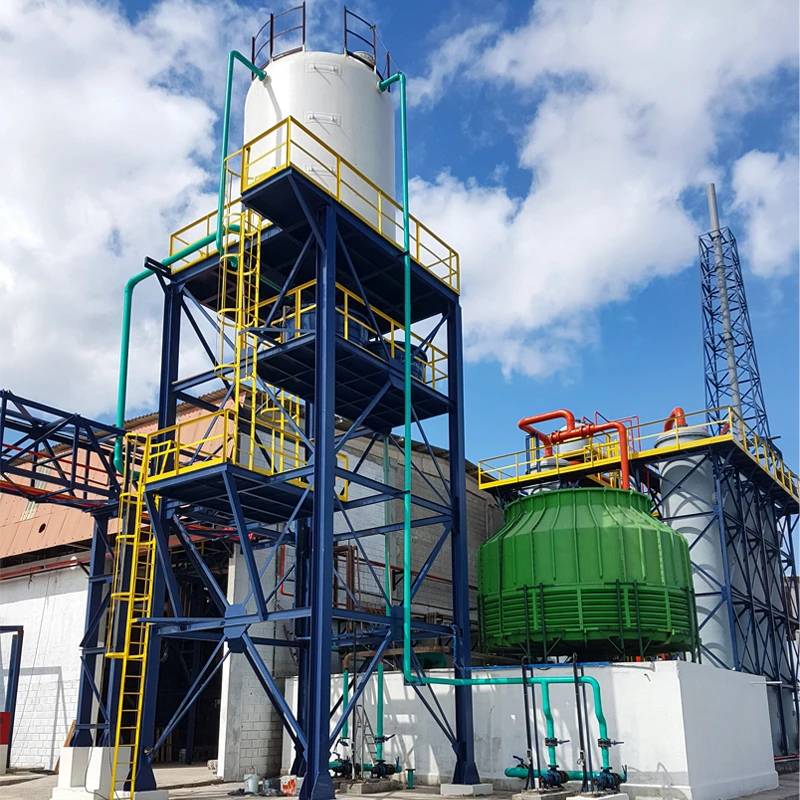
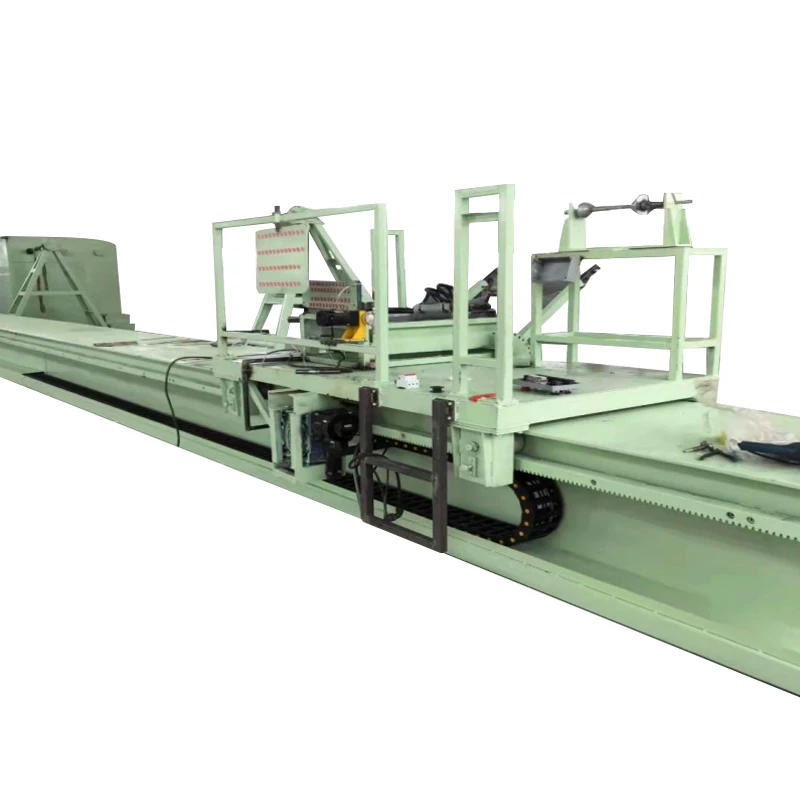
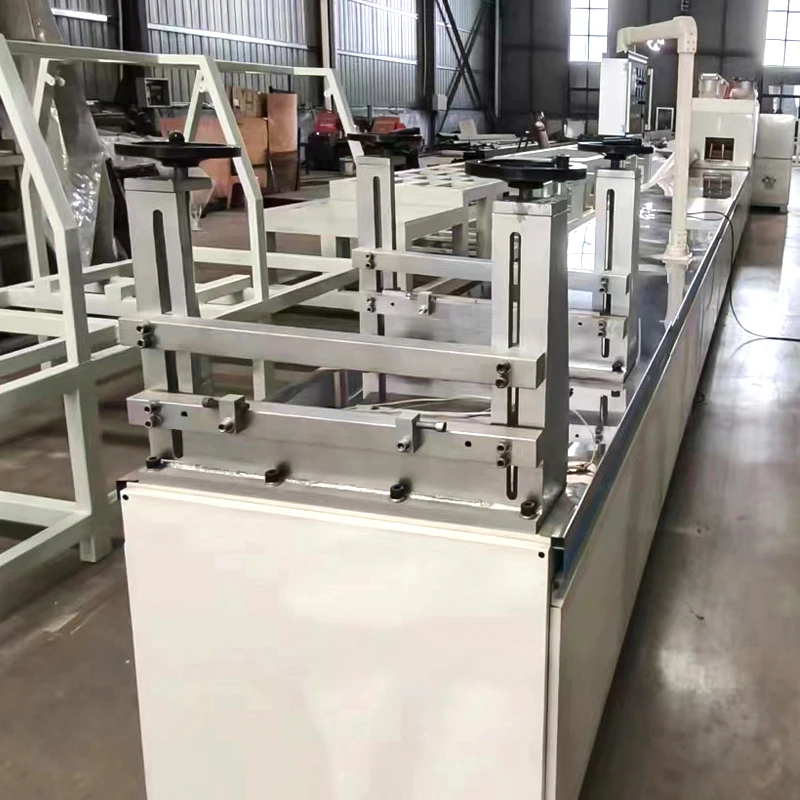
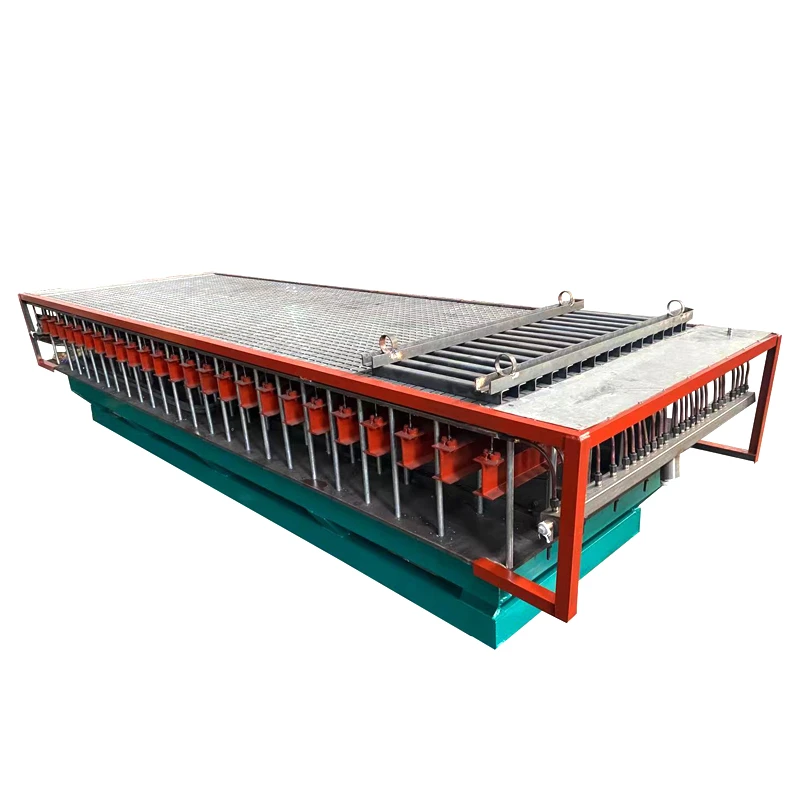
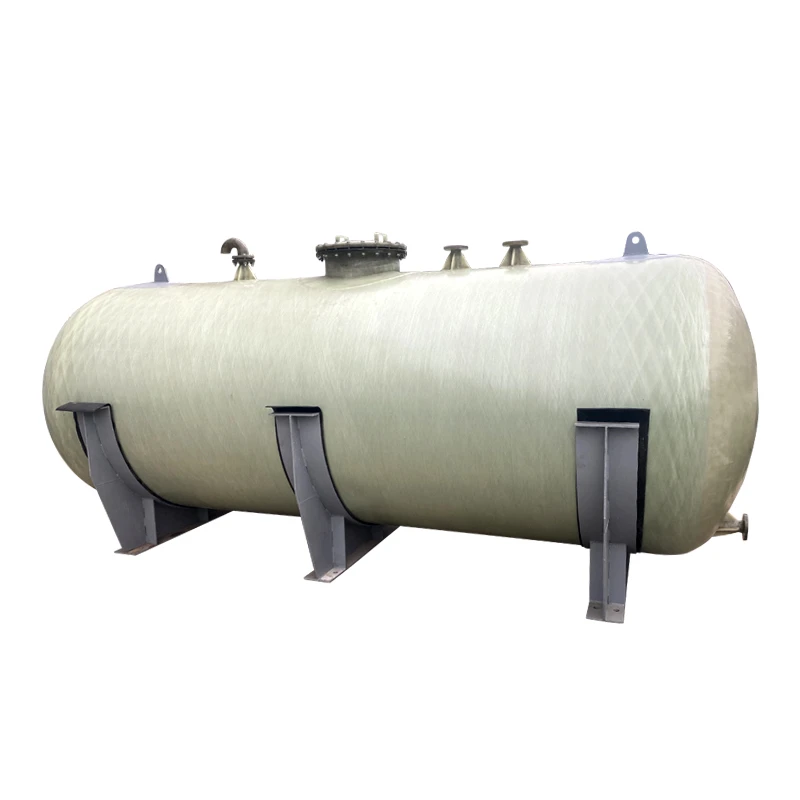
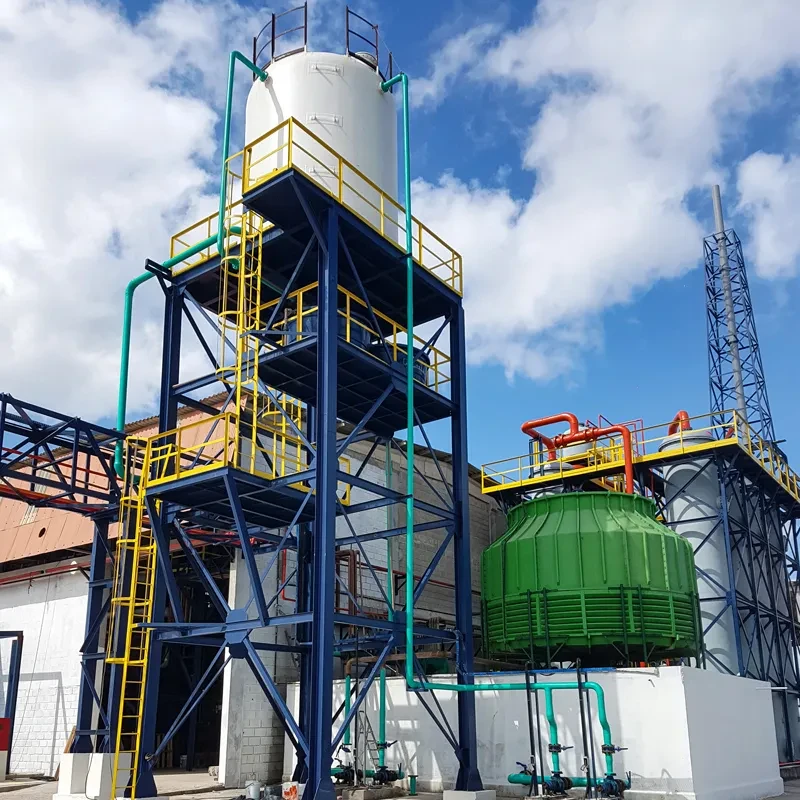
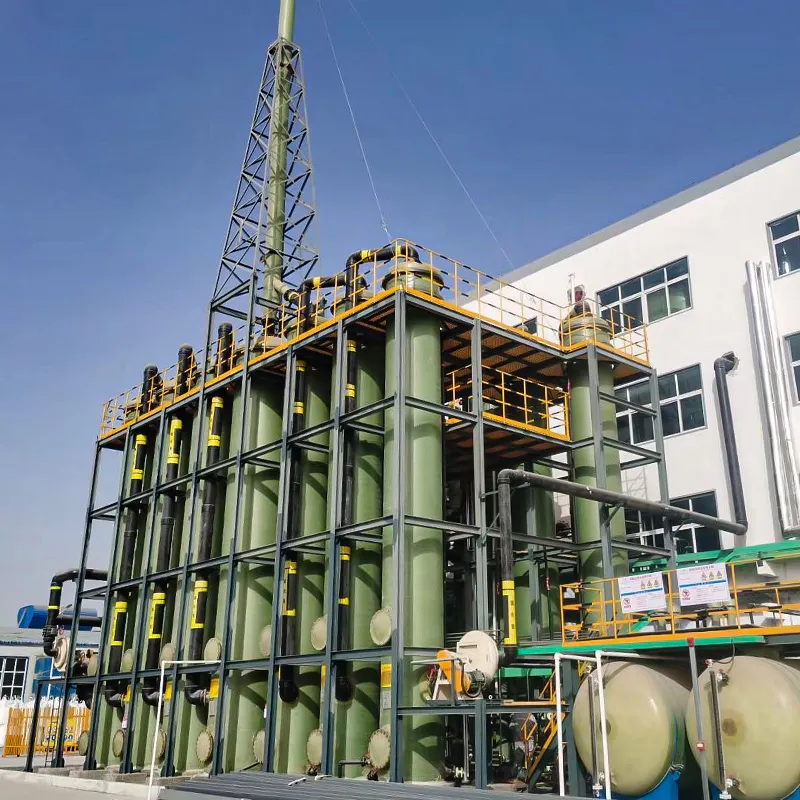
The basic structure of Mannheim Furnace usually includes a cylindrical or rectangular furnace body, built with acid and high temperature resistant bricks
The Mannheim furnace design is equipped with a rotating stirring device to improve the contact efficiency between reactants. During the operation, solid sodium chloride and concentrated sulfuric acid are continuously or intermittently added to the furnace, and the high temperature environment (about 500-600 degrees Celsius) is maintained by external heating or combustion of fuel. At high temperatures, sodium chloride reacts with sulfuric acid to produce sodium sulfate, while releasing hydrochloric acid gas. Hydrochloric acid gas can be used to produce hydrochloric acid products after cooling, absorption and other processes. And sodium sulfate is extracted, which can be further used for the extraction of sodium sulfate or other purposes.
The advantages of Mannheim Furnace lie in its relatively simple structure and low initial investment cost, making it a feasible choice for small-scale sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid production enterprises
In addition, it has strong adaptability to raw materials and can use sodium chloride of different purities. However, Mannheim Furnace also has some obvious drawbacks. Firstly, the reaction process generates a large amount of waste heat, resulting in low energy utilization efficiency. Secondly, the maintenance cost of the equipment is relatively high, as high temperatures and corrosive gases can easily cause damage to the furnace body and stirring device. Thirdly, some by-products and exhaust gases are generated during the production process, which require corresponding treatment to meet environmental protection requirements.
With the advancement of technology, modern Mannheim furnace design increasingly adopts more efficient and environmentally friendly production processes such as contact method and double contact double absorption method
These methods not only increase the production and purity of sulfuric acid, but also reduce energy consumption and pollution emissions. However, in some developing countries or specific application areas, Mannheim furnace design is still a viable option due to limitations in cost, technology, and other aspects. For example, some small chemical companies may choose to use Mannheim Furnace to produce hydrochloric acid for industries such as wastewater treatment or metal processing.
In summary, Mannheim Furnace, as a traditional production equipment for sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, occupies an important position in the history of industrial development. Although its efficiency and environmental performance are relatively low, it still has certain application value under specific conditions. With the continuous advancement of technology, the application scope of Mannheim Furnace may further shrink, but its historical significance and technological contribution in the chemical industry will still be remembered by people.
Mannheim Furnace FAQs
What is the main purpose of Mannheim Furnace?
It is mainly used for the production of potassium sulfate (K ₂ SO ₄), which combines potassium chloride (KCl) with concentrated sulfuric acid (H ₂ SO ₄) through high-temperature reaction, and is suitable for the chemical and fertilizer industries.
What is the working principle of Mannheim Furnace?
At high temperatures (approximately 500-600 ° C), potassium chloride reacts with sulfuric acid in a rotary furnace to produce potassium sulfate and byproduct hydrogen chloride gas (HCl), which can be recovered for use in other industrial processes.
What are the typical structural characteristics of Mannheim Furnace?
The core components include a corrosion-resistant lining rotary furnace, heating system (gas or electric heating), gas processing unit (such as HCl absorption tower), and automation control system.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Mannheim process?
Advantages: Potassium sulfate products have high purity, and the by-product HCl can be reused; Disadvantages: High energy consumption, high equipment maintenance costs, and the need to handle corrosive media.
How to utilize Mannheim Furnace by-product hydrogen chloride?
HCl gas is usually absorbed to produce hydrochloric acid, which is used for water treatment, metal cleaning, or chemical production to achieve resource recycling.