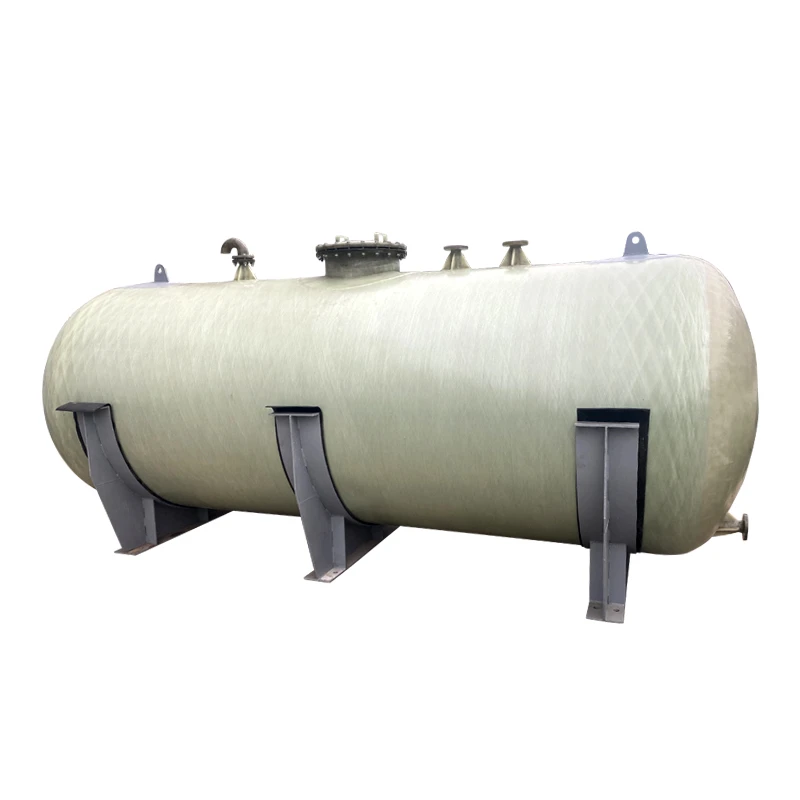
High-Quality Chemical Wash Tank Durable Chemical Injection & Reaction Tanks for Industrial Use
- Introduction to Chemical Wash Tanks and Related Equipment
- Key Technical Advantages
- Manufacturer Comparison: Data-Driven Insights
- Exploration of Customization Solutions
- Application Cases Across Industries
- Maintenance Best Practices and Safety Guidelines
- Conclusion: Future Innovations in Chemical Wash Tank Technology

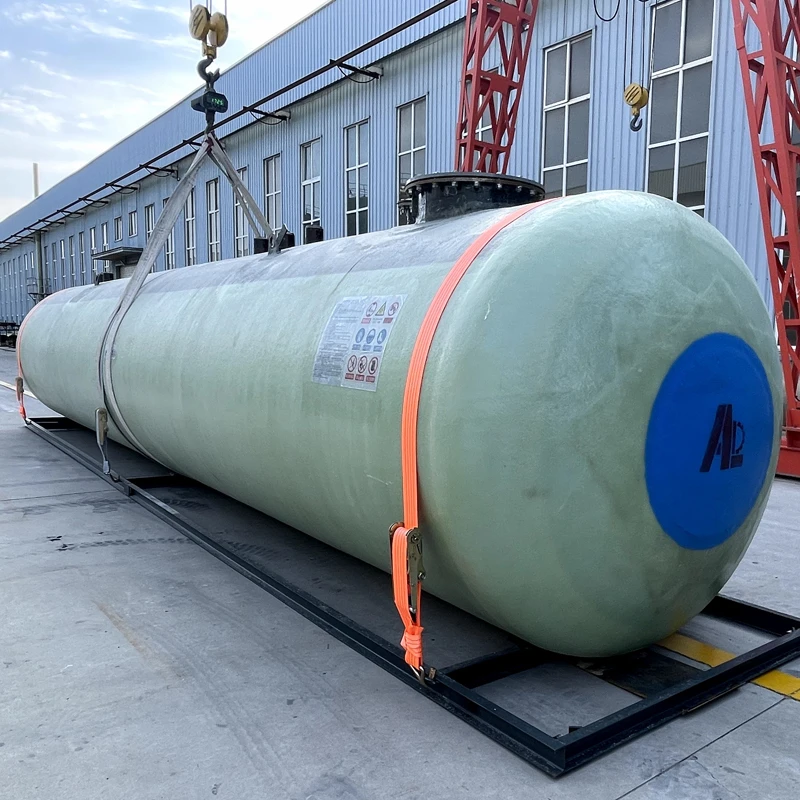
(chemical wash tank)
Introduction to Chemical Wash Tank Solutions
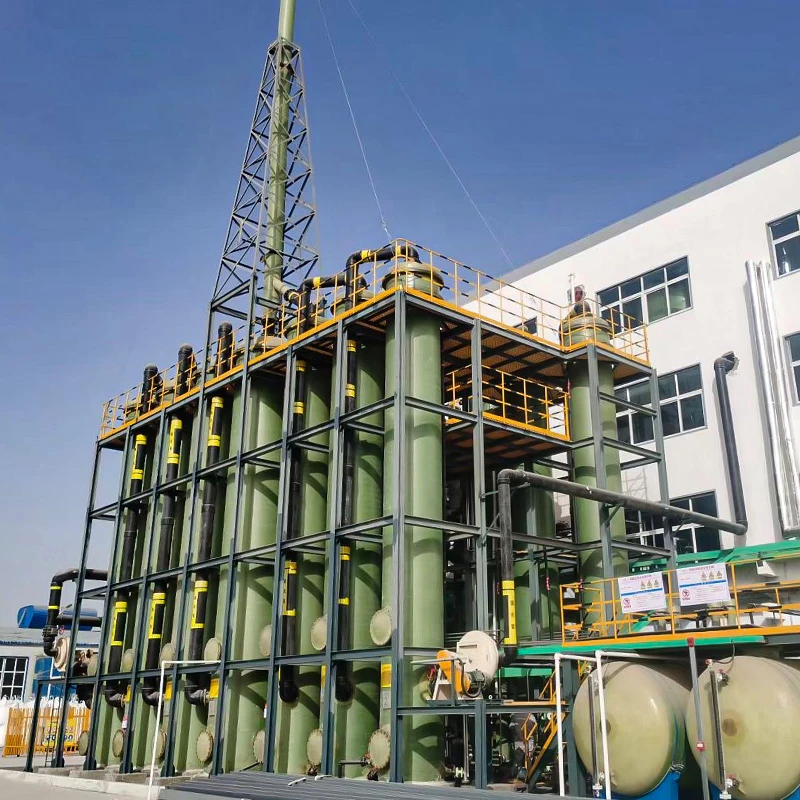
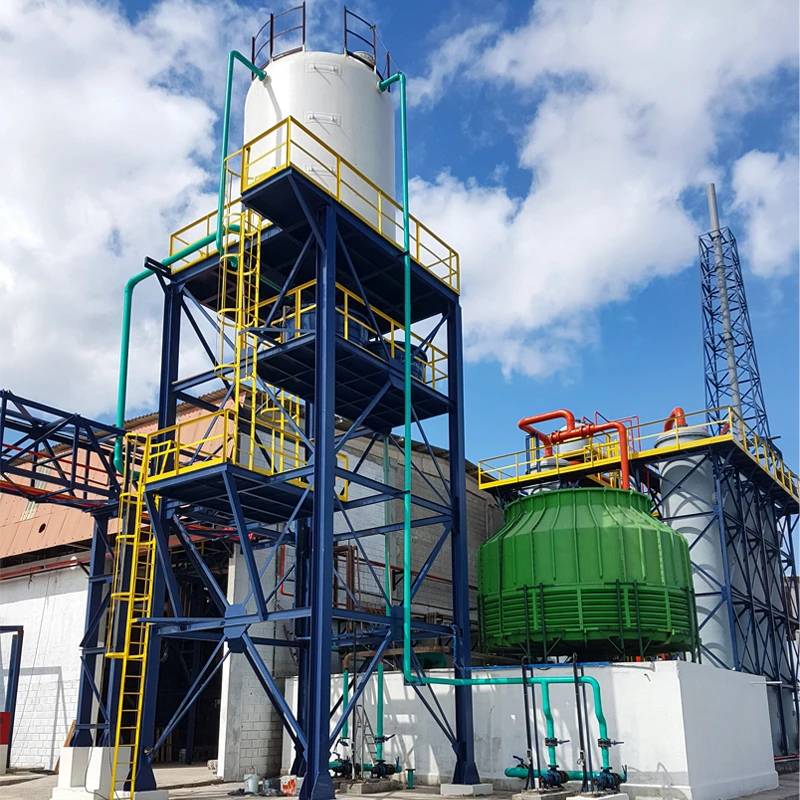
The industrial landscape relies heavily on specialized containment and processing systems to manage chemicals safely and efficiently. Among these, the chemical wash tank
has secured a pivotal role in diverse operations—ranging from large-scale petrochemical installations to pharmaceutical production lines. Modern chemical wash tanks often work in synergy with chemical injection tanks and chemical reaction tanks, together forming integrated fluid management solutions that meet stringent regulatory and operational specifications.
The global demand for such infrastructure has surged: according to Grand View Research, the industrial chemical tank market was valued at $1.6 billion in 2022, projected to achieve a CAGR of 6.2% through 2030. This growth is propelled by rapid industrialization, the rising complexity of chemical processes, and stricter environmental compliance regulations.
This article systematically explores the technological advancements behind chemical wash tanks, compares leading suppliers through data analysis, outlines custom-build opportunities, and presents practical application cases, illuminating the crucial choices that define a plant’s reliability and performance.
Technical Advancements in Chemical Tank Engineering
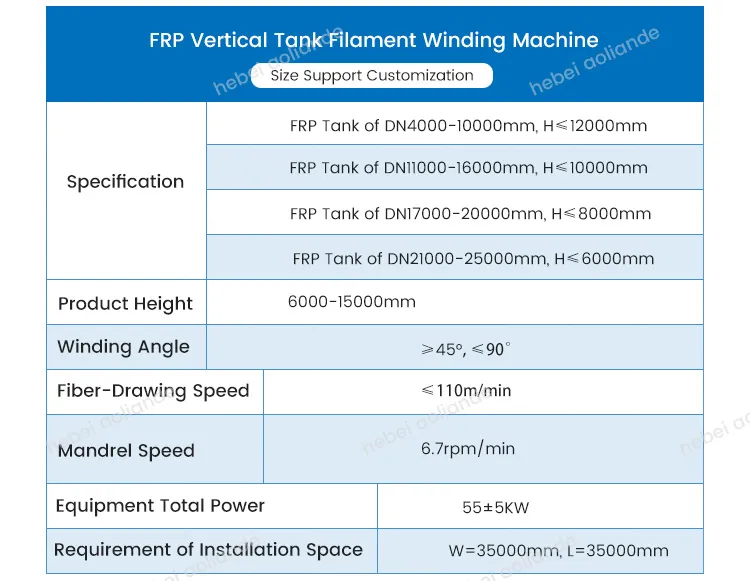
In recent years, chemical wash tank technology has evolved beyond basic containment—focusing on operational safety, longevity, and cost-efficiency. Leading tanks are fabricated from high-grade materials such as HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene), FRP (Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic), and duplex stainless steel, boasting corrosion resistance up to 99% against a broad spectrum of aggressive chemicals.
Enhanced features—like automated dosing systems, built-in level monitoring, and self-cleaning nozzles—help minimize manual intervention, reducing overall human error risk by up to 70%. Notably, temperature control modules support process consistency during chemical reactions, especially when tanks integrate with chemical injection or reaction systems.
According to a 2023 industry survey, plants utilizing advanced tank monitoring report a 30% reduction in chemical loss incidents annually. In summary, technical breakthroughs in tank fabrication and monitoring are reshaping operational risk management and production efficiency standards.
Manufacturer Comparison: Market Data and Performance Benchmarks
Selecting the right provider is paramount, as quality variations can significantly impact both operational safety and lifecycle cost. The following table presents a comparative analysis of top global manufacturers in the chemical tank domain, specifically focusing on chemical wash tank offerings:
| Manufacturer | Country | Core Material | Warranty (Years) | Certifications | Avg. Delivery Time (Days) | User Satisfaction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Tanks Ltd. | USA | HDPE, SS316L | 5 | ASME, ISO 9001 | 28 | 95.6 |
| EcoChem Systems | Germany | FRP, PE | 7 | TUV, ISO 14001 | 34 | 91.2 |
| Global Tank Solutions | UK | Stainless Steel | 10 | CE, PED | 40 | 92.7 |
| AsiaChem Equipco | China | PP, FRP | 3 | ISO 9001, SGS | 27 | 88.4 |
The data illustrates that warranties, certifications, and customer satisfaction rates are key differentiators when selecting a chemical wash tank supplier; for example, Global Tank Solutions provides the longest warranty at 10 years, whereas XYZ Tanks Ltd. leads in customer satisfaction.
Customization Options: Meeting Specific Industry Needs
No two process facilities are identical, making customization a critical element in the design and procurement of chemical wash tanks. Leading manufacturers offer a spectrum of tailored options—capacity ranging from small 50-liter vessels for laboratory use up to 50,000-liter tanks for municipal water treatment. Material selection is guided by chemical compatibility charts, ambient operating temperatures, and targeted pressure ratings.
Design modifications may include double-walled containment for leak prevention, integrated mixing mechanisms for homogeneous chemical blending, or multi-chamber tanks supporting sequential injection and reaction phases.
Furthermore, digital integration possibilities such as IoT-enabled sensors provide real-time tank telemetry, alerting operators to anomalies within seconds. Customization, thus, goes beyond form factors—it encompasses smart engineering and process integration, underscoring the commitment to both safety and process optimization.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Chemical Tank Systems
Chemical wash tanks, in concert with chemical injection and reaction tanks, demonstrate their performance in diverse sectors:
- Oil & Gas: In a major Middle Eastern oilfield, FRP tanks with automated pH adjustment reduced scale formation in pipelines by 40%, translating to a $1.2 million yearly operational saving.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Integrating HDPE chemical tanks with advanced dosing pumps enabled a European client to maintain product purity levels above 99.8%, crucial for API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) synthesis.
- Municipal Water Treatment: AsiaChem Equipco provided double-walled PE tanks that helped a metropolitan authority meet stricter chloride discharge regulations, improving compliance rates from 82% to 96% within nine months.
- Food Processing: Stainless steel wash and reaction tanks ensured residue-free sanitation, reducing contamination risk by an estimated 78%, while extending cleaning cycles by 20%.
Maintenance Protocols and Safety Standards
To uphold the operational viability and safety of chemical wash, injection, and reaction tank installations, strict maintenance regimes must be embedded as standard practice. Weekly and monthly inspection schedules typically include visual checks for structural integrity, assessment of vent and drain functions, and verification of sensor performance. Data from a 2021 benchmarking study found that facilities adhering to ISO 45001 safety management systems experienced 45% fewer chemical tank-related incidents than those without certified protocols.
Comprehensive cleaning routines—utilizing in-line flushing or CIP (Clean-In-Place) systems—can extend tank lifespan by 30% on average, while reducing cross-contamination risks. Staff training and routine safety drills are vital; proficient teams can manage minor leaks or system alarms within five minutes, significantly mitigating environmental or operational harm. Alignment with ASME and OSHA guidelines further cements safety and compliance.
Conclusion: The Evolving Future of Chemical Wash Tank Technologies
As industries continue to demand safer, greener, and smarter fluid management systems, the chemical wash tank segment is set for rapid and ongoing innovation. Emerging trends include the integration of AI-driven predictive maintenance, use of recycled composite materials, and the adaptation of fully automated dosing and monitoring systems.
Furthermore, as digitalization penetrates industrial infrastructure, remote control capabilities and cloud-based performance analytics will move from optional assets to expected standards. The synergy among chemical wash tank, injection, and reaction tank technologies not only addresses today’s compliance and efficiency needs but also sets the stage for future-proof solutions.
By balancing rigorous customization, robust safety, and cutting-edge process integration, manufacturers and end-users alike are poised to redefine reliability and operational excellence in chemical management for decades to come.
(chemical wash tank)