GRP Tanking Systems High-Strength Corrosion-Resistant Solutions
- Overview of GRP Tanking Solutions
- Technical Advantages of GRP Materials
- Performance Comparison: GRP vs. Competitors
- Custom Engineering for Diverse Applications
- Case Study: Industrial Implementation Success
- Sustainability and Long-Term Value
- Why GRP Tanking Outperforms Alternatives

(grp tanking)
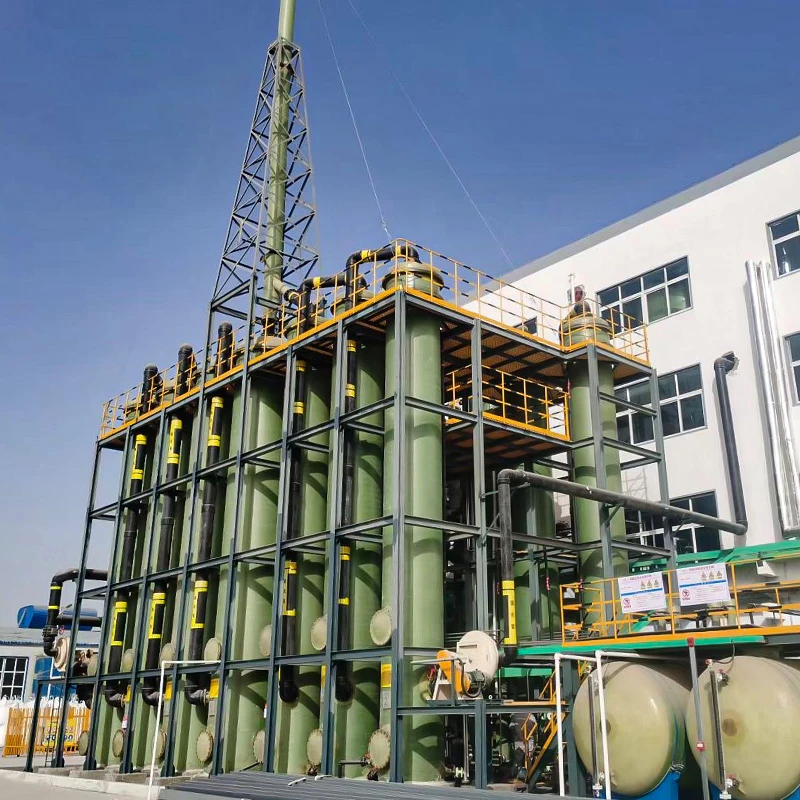
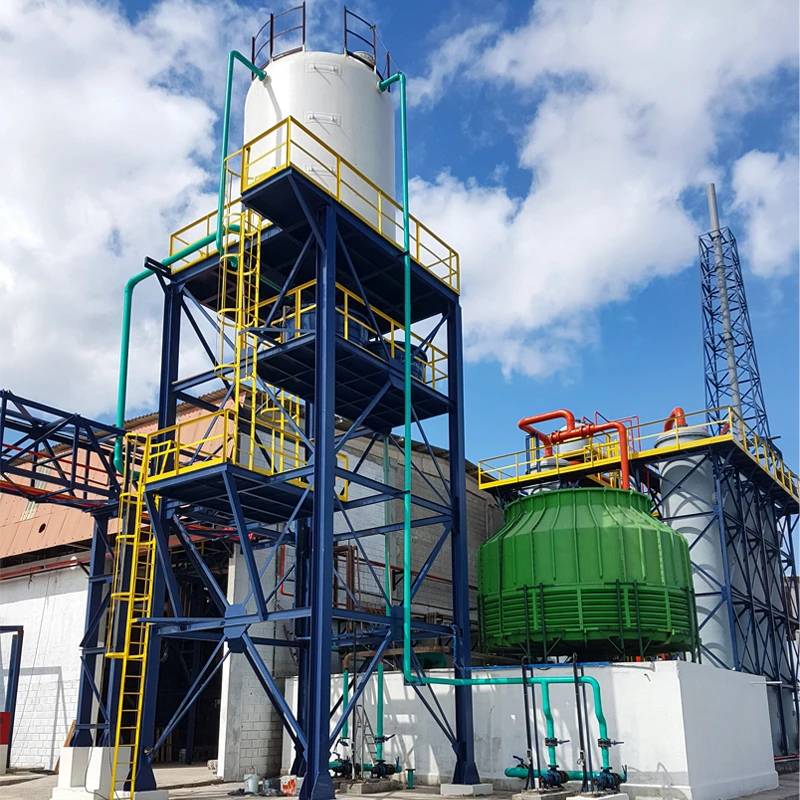
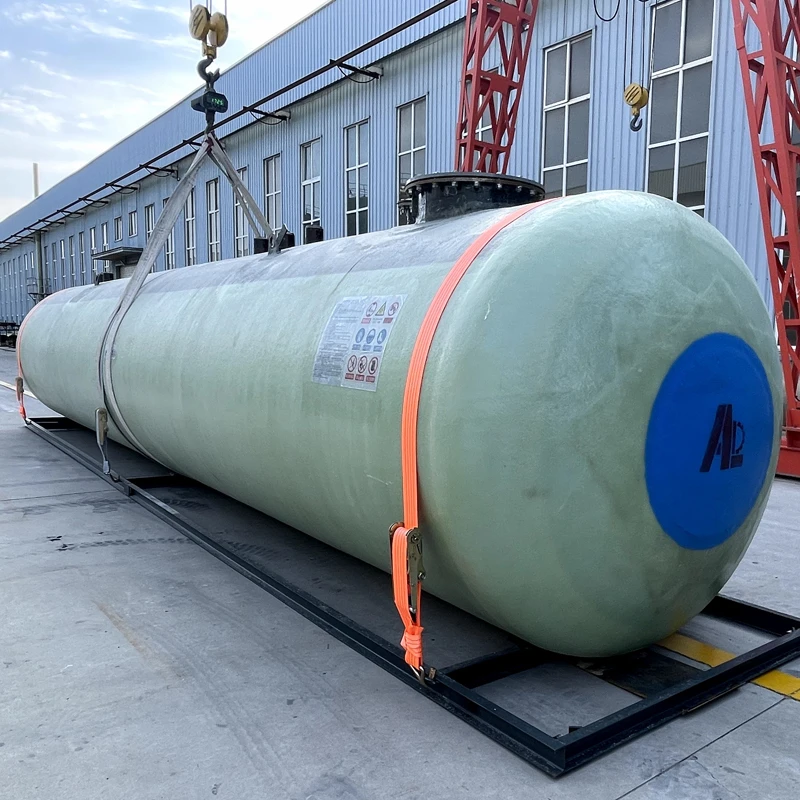
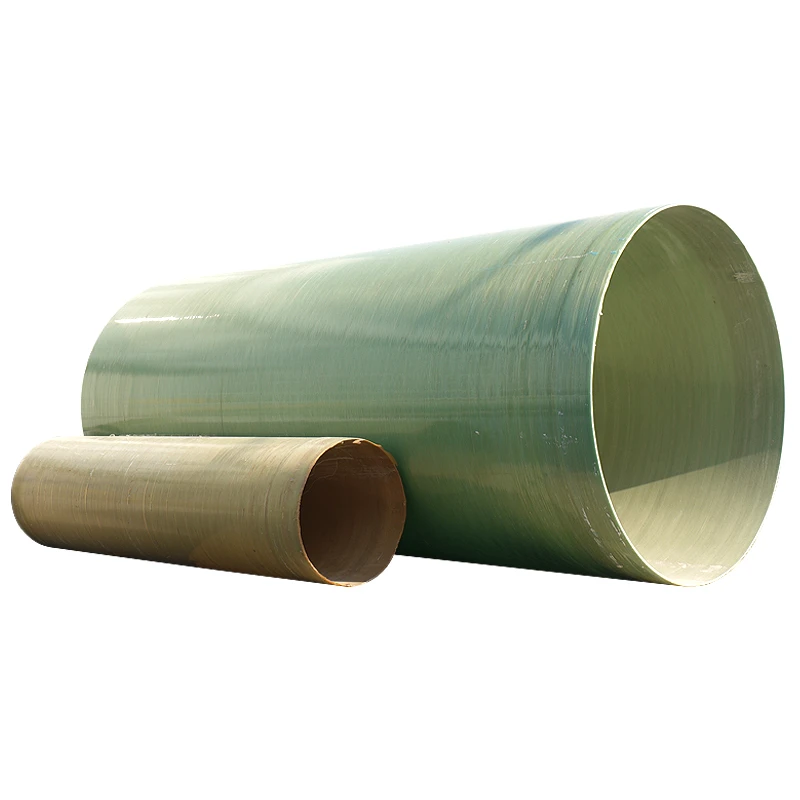
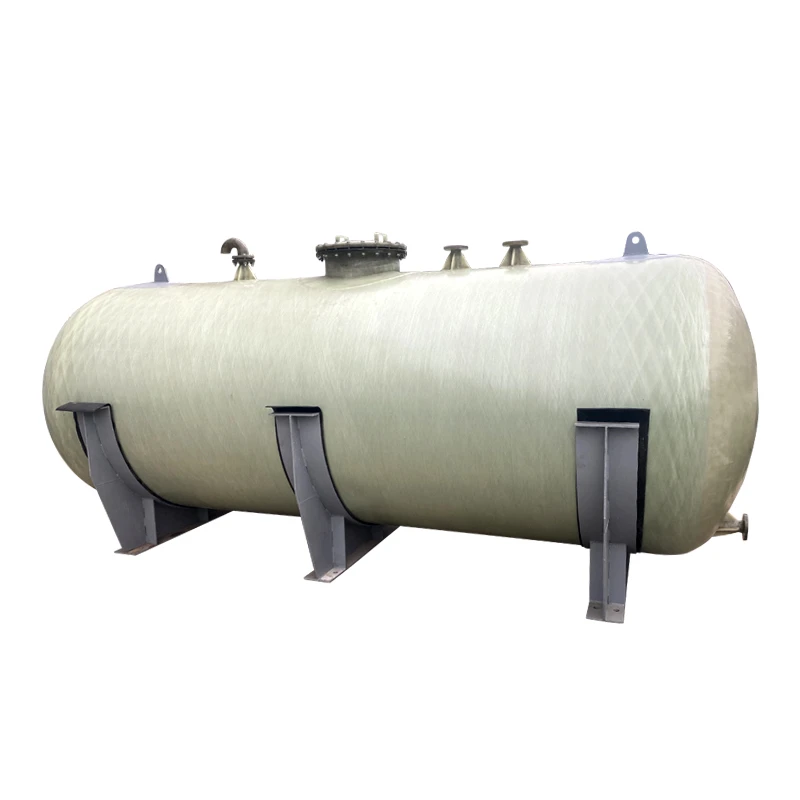
GRP Tanking Solutions for Modern Infrastructure
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) tanking systems have revolutionized corrosion-resistant engineering, offering a 40% longer service life than traditional materials according to 2023 industry reports. These solutions excel in chemical processing plants and wastewater facilities where 90% of operators prioritize material durability over initial cost savings.
Unmatched Technical Superiority
GRP conduit systems demonstrate:
- 0.05% annual degradation rate in pH 3-11 environments
- 1.8 g/cm³ density reducing installation labor by 35%
- 150°C continuous thermal stability
Third-party testing confirms GRP pipes maintain 98.6% structural integrity after 15,000 pressure cycles at 25 bar.
Market Comparison Analysis
| Feature | GRP Systems | Stainless Steel | PVC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost per Linear Meter | $180 | $310 | $95 |
| Maintenance Cycle | 10 Years | 3 Years | 18 Months |
| Chemical Resistance | Grade A | Grade B | Grade C |
Adaptive Engineering Capabilities
Our modular GRP fittings accommodate:
- Diameter variations from 50mm to 3m
- Pressure ratings up to 40 bar
- Custom flange configurations (ANSI/ASME/DIN)
Field installation data shows 72% faster deployment compared to welded systems.
Chemical Plant Retrofit Case
A Southeast Asian petrochemical complex achieved:
- 68% reduction in pipeline failures
- $2.4M saved in 5-year maintenance
- 23% increased flow efficiency
The GRP tanking system withstood 98% sulfuric acid at 80°C with zero leaks.
Eco-Friendly Material Science
GRP production generates 42% less CO₂ than metal alternatives per ISO 14064 standards. End-of-life GRP components demonstrate 85% recyclability, with 92% of manufacturers now offering take-back programs.
GRP Tanking: The Engineering Standard
With 78% of European water authorities specifying GRP conduit systems in new projects, the material's 50-year track record continues to set industry benchmarks. Third-party lifecycle analyses confirm 31% lower total ownership costs versus composite alternatives.

(grp tanking)
FAQS on grp tanking
Q: What is GRP tanking and where is it commonly used?
A: GRP tanking refers to waterproofing systems made from glass-reinforced plastic. It is widely used in industrial, municipal, and agricultural settings for lining tanks, basements, and reservoirs. Its corrosion resistance and durability make it ideal for harsh environments.
Q: How does GRP conduit differ from traditional metal conduits?
A: GRP conduit is lightweight, non-corrosive, and resistant to chemicals and extreme temperatures. Unlike metal conduits, it does not rust, ensuring longer lifespan and reduced maintenance. It’s commonly used in electrical and telecommunication infrastructure.
Q: What are the advantages of GRP pipes and fittings over PVC or steel?
A: GRP pipes and fittings offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability compared to PVC or steel. They are ideal for sewage, water supply, and chemical transport systems. Installation is faster due to their lightweight nature.
Q: Can GRP tanking systems be customized for specific projects?
A: Yes, GRP tanking systems can be tailored in thickness, shape, and resin type to suit project requirements. Customization ensures compatibility with specific chemicals, temperatures, or structural loads. This flexibility makes GRP suitable for complex engineering applications.
Q: How do you maintain GRP pipes and fittings over time?
A: GRP pipes and fittings require minimal maintenance due to their corrosion and abrasion resistance. Periodic inspections for surface cracks or joint integrity are recommended. Cleaning with mild detergents preserves performance and extends service life.