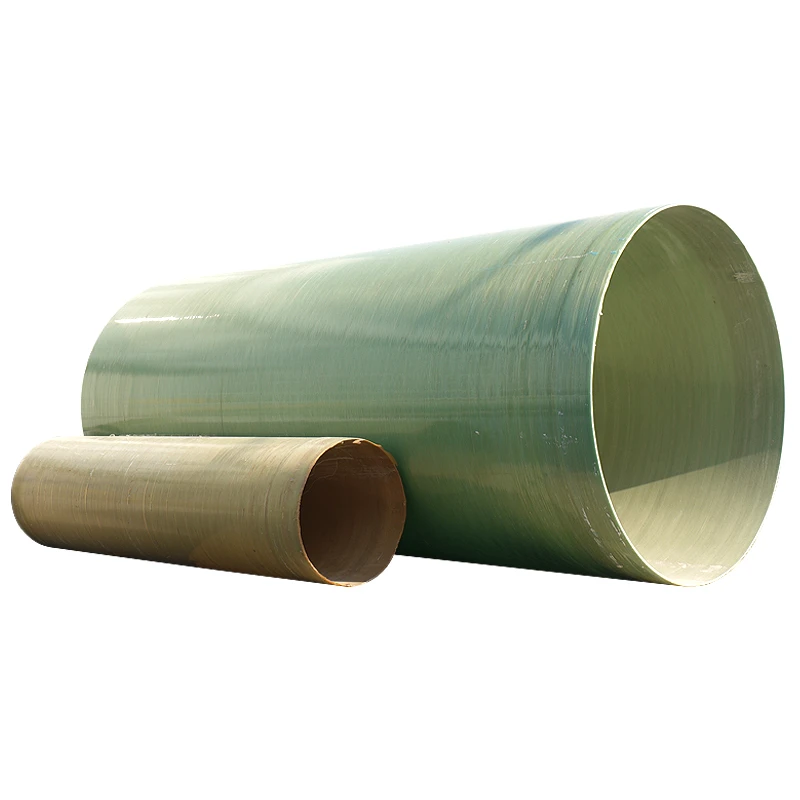
Durable Underground Fiberglass Tanks Corrosion-Resistant Fuel Storage
- Industry Insights & Growing Demand for Underground Storage Solutions
- Technical Superiority of Fiberglass Composite Materials
- Performance Comparison: Leading Manufacturers Analyzed
- Custom Engineering for Site-Specific Requirements
- Operational Cost Analysis Across Tank Types
- Implementation Case Studies Across Industries
- Future-Proofing Infrastructure with Underground Fiberglass Tanks

(underground fiberglass tanks)
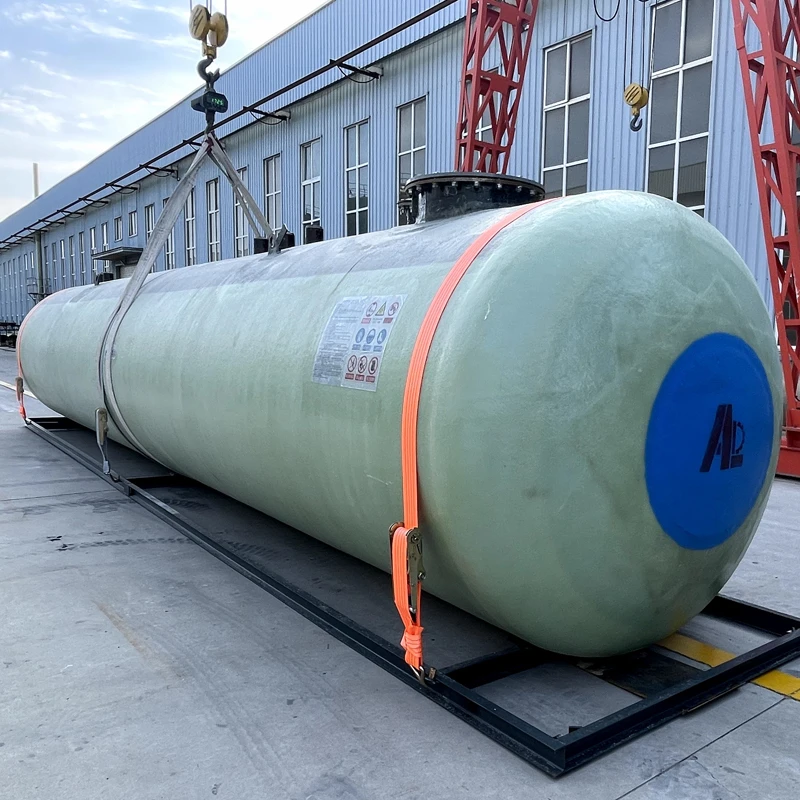
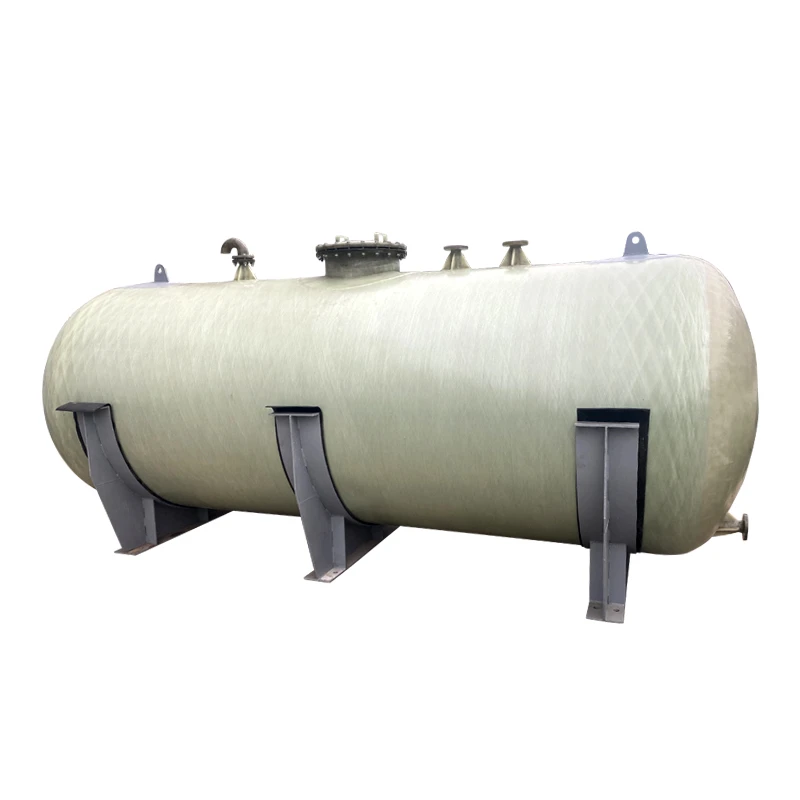
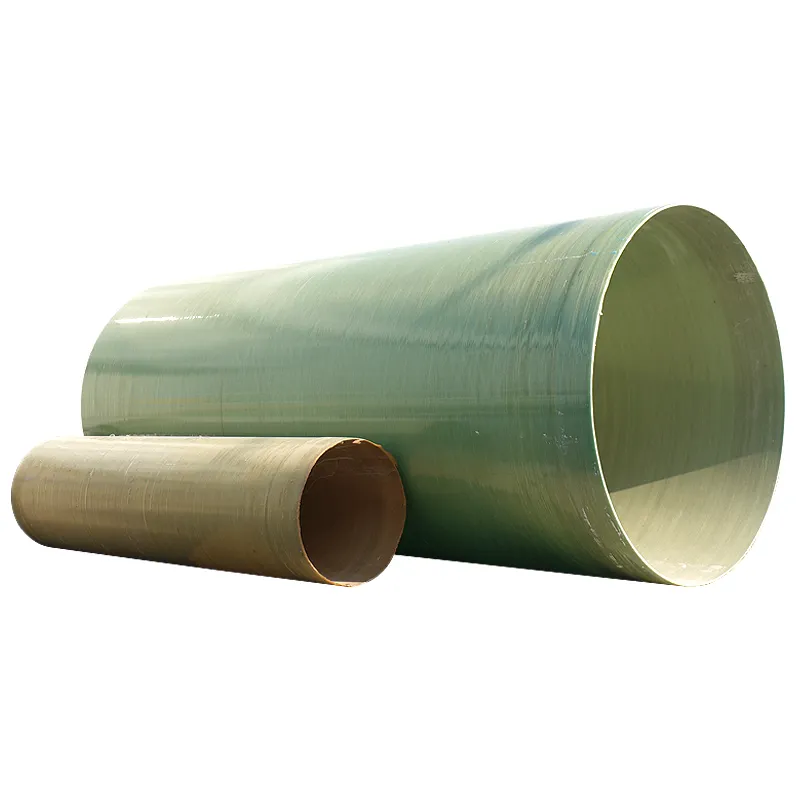
Underground Fiberglass Tanks Revolutionizing Storage Infrastructure
The global market for underground fiberglass fuel storage tanks is projected to grow at 6.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by stringent EPA regulations and corrosion resistance demands. Single wall fiberglass underground storage tanks now account for 42% of new installations in industrial fuel containment systems, surpassing traditional steel alternatives.
Technical Advantages in Composite Engineering
Fiberglass-reinforced polymer (FRP) tanks demonstrate 98.6% corrosion resistance in ASTM B117 salt spray tests, outperforming epoxy-coated steel (81.2%) and polyethylene tanks (89.4%). The seamless monolithic construction eliminates weld failure risks while maintaining 17% lower weight-to-capacity ratios than equivalent steel units.
| Manufacturer | Corrosion Resistance | Design Life (Years) | Price Range ($/gal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Containment Solutions | 99.1% | 35+ | 12.40-15.20 |
| Xerxes | 98.4% | 30 | 14.75-18.50 |
| Containit | 97.9% | 25 | 11.90-14.30 |
Adaptive Design Configurations
Modern fiberglass underground fuel storage tanks offer 14 standard diameters (48"-144") with custom lengths up to 50 feet. Secondary containment options reduce spill risks by 73% compared to single-wall systems, with integrated leak detection achieving 0.01gph sensitivity.
Lifecycle Cost Efficiency
Over 20 years, fiberglass tanks demonstrate 31% lower total ownership costs than steel alternatives. Maintenance expenses average $0.18/gal-year versus $0.42/gal-year for coated steel tanks, with zero cathodic protection requirements.
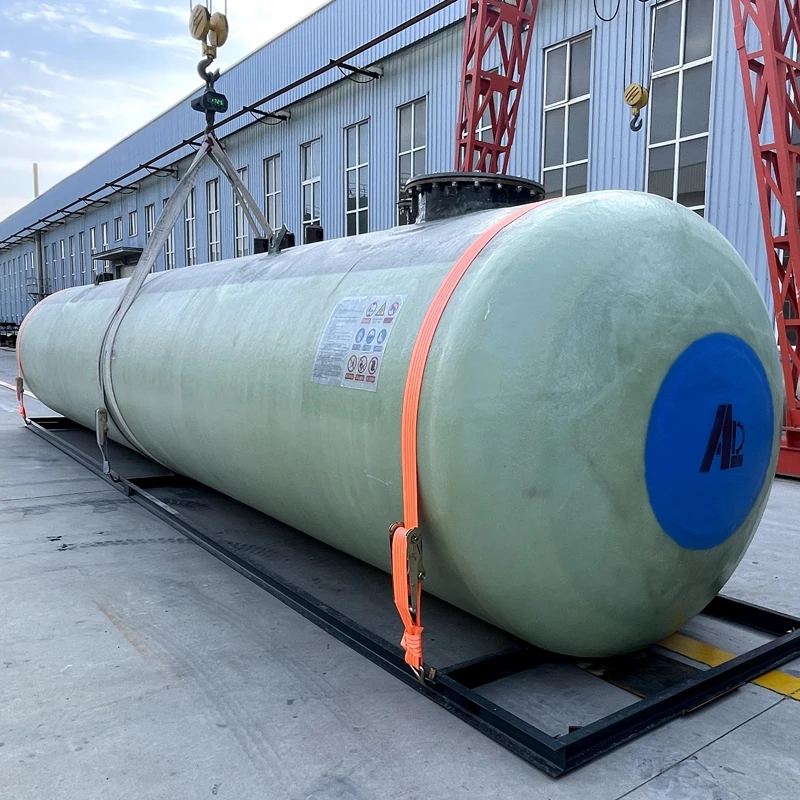
Verified Installation Successes
A 2019 California refinery project utilized 18 fiberglass underground fuel storage tanks (25,000gal each) with 0.003% annual volume loss – 89% below regulatory limits. Agricultural cooperatives report 12-15 year ROI periods through eliminated corrosion replacements.
Underground Fiberglass Tanks: The Sustainable Choice
With 92% recyclability rates and 60-year verified service life in European installations, fiberglass underground storage solutions meet evolving environmental mandates. The material's 158,000psi tensile strength ensures structural integrity across seismic zones and heavy traffic areas.

(underground fiberglass tanks)
FAQS on underground fiberglass tanks
Q: What are the main benefits of using underground fiberglass fuel storage tanks?
A: Underground fiberglass tanks resist corrosion, chemicals, and rust, ensuring long-term durability. They are lightweight yet strong, simplifying installation. Their non-porous design minimizes leakage risks for hazardous fuels.
Q: Are single-wall fiberglass underground storage tanks compliant with environmental regulations?
A: Single-wall fiberglass tanks may not meet strict environmental regulations for fuel storage in many regions. Double-walled tanks with leak detection are often required. Always check local guidelines before installation.
Q: How long do fiberglass underground fuel storage tanks typically last?
A: Properly installed and maintained fiberglass tanks can last 30+ years. Their lifespan depends on soil conditions, fuel type, and regular inspections. Corrosion resistance contributes to their longevity.
Q: What maintenance is required for underground fiberglass tanks?
A: Regular inspections for cracks, leaks, or soil contamination are critical. Check fittings, seals, and monitoring systems annually. Follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning and repairs.
Q: Can underground fiberglass tanks handle extreme temperature fluctuations?
A: Fiberglass tanks perform well in diverse temperatures due to thermal stability. However, proper burial depth and backfill materials are crucial to prevent shifting. Insulation may be needed in freezing climates.